Many of the modern brands producing PC hardware components, as well as software, strive to ensure that their products support the UEFI interface. This software solution is intended to become an alternative to the input-output system - BIOS - that is familiar to many computer enthusiasts. What are the specifics of the software in question? What nuances are typical for using its capabilities?
What is UEFI
Let's look at some basic information about UEFI. What kind of development is this? UEFI is a special interface that is installed between the OS installed on the computer and the software responsible for the low-level functions of the PC hardware components.
Sometimes referred to as UEFI BIOS. On the one hand, there is some error in this name, since BIOS is a software solution that operates on different principles. UEFI is developed by Intel, BIOS is software that exists in several versions supported by different brands.
On the other hand, the purpose of BIOS and UEFI is almost the same. BIOS UEFI is a formal, not entirely correct phrase, but it does not contradict the logic of software and hardware algorithms for PC control.
Differences between BIOS and UEFI
But the first thing we will pay attention to is finding the differences between a “clean” BIOS and a “classic” UEFI. The fact is that the software solution we are considering is positioned as a more advanced alternative to BIOS. Many manufacturers of modern computer motherboards are trying to provide support for the appropriate type of software from Intel. Thus, we can trace the differences between UEFI and BIOS by studying, first of all, the shortcomings of the second system.

The first disadvantage of BIOS is that this system cannot ensure full use of disk space on very large “hard drives” - those that exceed 2 terabytes in volume. Indeed, just a few years ago, such values characterizing the capacity of hard drives seemed fantastic, and therefore PC manufacturers did not particularly focus on the corresponding drawback of the BIOS. But today you won’t surprise anyone with a hard drive with a capacity of more than 2TB. PC manufacturers began to feel that it was time to switch to UEFI, that this was an objective necessity based on modern technological trends.
Another feature of BIOS is that it supports a limited number of primary partitions on the hard drive. In turn, UEFI works with 128. The structure of the new software solution from Intel implements a new partition table - GPT, which, in fact, allows you to use the noted technological advantage of UEFI.

With all the noted differences between the new software environment developed by Intel and the traditional BIOS input/output system, the main functions of the corresponding solutions are generally the same. Apart from the fundamentally new security algorithm in UEFI, there are not too many actual differences between the systems. Some experts believe that the new software platform allows operating systems to boot faster, others note that this is only relevant for Windows 8. Let's take a closer look at the security system implemented in UEFI.
New security technology
Where the new UEFI BIOS system is ahead is in the level of security. The fact is that there are viruses that can penetrate the microcircuit where the BIOS algorithms are written. After which, it becomes possible to load the OS with extended user rights, which opens up the widest possible opportunities for a hacker. In turn, the new solution from Intel implements secure boot - UEFI provides an appropriate algorithm called Secure Boot.
It is based on the use of special keys, which must be certified by the largest brands in the IT market. However, as experts note, in practice there are not too many such companies yet. In particular, with regard to the support of the corresponding option by operating system manufacturers, it is fully provided only by Microsoft and only in Windows 8. There is also information that compatibility with the new security system is implemented in some Linux distributions.
Benefits of UEFI
It is obvious that the noted disadvantages of the BIOS are, at the same time, the advantages of the new software solution. However, UEFI is characterized by a number of other important advantages. Let's look at them.
First of all, it is a convenient, intuitive and functional interface. As a rule, it implements mouse support - which is not typical for BIOS. Also, many versions of UEFI (BIOS does not have this option either) provide a Russified interface.
The algorithms provided by the new software solution allow loading operating systems in most cases significantly faster than when using BIOS. For example, Windows 8 installed on a UEFI-enabled computer can boot—provided the processor and other key hardware components have adequate performance—in literally 10 seconds.
Among other significant advantages of the software solution in question, which many IT specialists highlight, is a simpler update algorithm compared to BIOS mechanisms. Another useful UEFI option is that a given system has its own, which can be used if several operating systems are installed on the PC.
So, the technological advantages of the new PC management software interface, which was developed by Intel, are clear to us. The largest brands of PC hardware components ensure compatibility of the corresponding hardware with UEFI - Gigabyte, ASUS, SONY. The transition to a new system, as many IT experts believe, can turn into a sustainable technology trend. The opportunities offered to the global IT community by Intel, which developed UEFI, may well be attractive to leading manufacturers of software and hardware components for PCs. Moreover, the corresponding UEFI technological options are supported by the largest brand in the operating system market.
Facts about Secure Boot
Let's take a closer look at the advantages of Secure Boot technology supported by UEFI. What is this concept? safe booting of the computer, which is designed to protect the system, as we noted above, from the penetration of viruses. However, for its full use, the keys used by this protocol must be certified. At the moment, very few software brands satisfy this criterion. Among these is Microsoft, which has implemented support for the corresponding algorithms in Windows 8.

It may be noted that this circumstance in some cases can complicate the installation of other operating systems on a PC running UEFI. If you have to install Windows, UEFI may still show some loyalty to this - but provided that the OS version is as close as possible to the one installed by the computer manufacturer. It may also be noted that some Linux distributions are also compatible with the Secure Boot option.
But even if, due to the function in question, loading a new OS is prohibited by the system, the structure of the UEFI interface provides the ability to disable Secure Boot algorithms. It is clear that in this case, loading the OS will not be so safe, however, the corresponding option can be reactivated at any time and start working with Windows 8.
Which OS are fully UEFI compatible?
In very rare cases, individual IT specialists manage to install alternative operating systems on a PC with Secure Boot support. For example, it is known that it is theoretically possible to install Windows 7 on some laptops that support UEFI BIOS. ASUS is among the manufacturers of such PCs. But this is rather an exception to the rule. In general, the probability of successful installation of even other editions of Windows 8 is low. However, as we noted above, some Linux distributions are also compatible with UEFI options.
Features of UEFI setup
Let's look at some of the nuances of setting up the software solution in question from Intel. An interesting option is BIOS emulation using UEFI. What is this opportunity? Indeed, some versions of UEFI implement algorithms by which PC management is organized in accordance with the mechanisms used by the input/output system, which is the historical predecessor of UEFI.

Depending on the specific PC, this mode may be called differently. Most often this is Legacy or Launch CSM. However, there are no difficulties with how to install UEFI in standard boot mode.
Nuances of accessing UEFI
Another interesting fact that is useful to note is that there are a large number of versions of UEFI. They can vary significantly between PCs made by different brands. At the same time, the level of availability of certain functions on different computers can also vary significantly. It often happens, for example, that when the computer boots, the menu with which you can enter the UEFI settings is not displayed. But in this case, Windows OS usually provides an alternative option for downloading the necessary options. You need to go to “Settings” and activate the “Special boot options” option.

After this, you can reboot - and several options for loading your PC will appear on the screen. There is an alternative way to provide access to the appropriate UEFI options. It works on many PCs. You need to press Esc at the very beginning of the computer boot. After this, the menu in question should open.
Specifics of operation in different modes
Please note that when changing the normal UEFI operating mode to Legacy, it is advisable to use the necessary programs that require disabling Secure Boot or working with BIOS emulation, and re-enable the UEFI interface with all the corresponding options as soon as possible. Otherwise, Windows 8, as some IT specialists note, may not start. However, many PCs do not have this problem. Some manufacturer brands implement algorithms into the PC management structure that allow you to activate the UEFI mode automatically. Some PC models implement a hybrid mode, in which the UEFI system boots from any media, and BIOS modulation can be started if necessary. Differences in UEFI versions may also mean that disabling Secure Boot in the normal operation mode of the Intel software solution is not possible. To do this, you will have to activate the BIOS emulation function in any case.
UEFI and bootable flash drives
In some cases, users need to boot the operating system from a flash drive. The main difficulty is that a UEFI bootable flash drive having a format other than FAT32 is not recognized. But this problem can be successfully resolved. How?

So, by default, bootable USB flash drives for Windows are formatted in a format that UEFI does not recognize. Therefore, the main task is to ensure that the corresponding hardware component is formatted in the more universal file system - FAT32. The most interesting thing is that many IT specialists consider it outdated. But using the example of one of the most modern software solutions, which is, of course, UEFI, we can trace the relevance of the corresponding standard.
Flash drive for booting in UEFI mode: components
What do we need to ensure that the UEFI bootable flash drive is recognized without problems? First of all, this is, in fact, a USB drive itself. It is advisable that its capacity be at least 4 GB. It is also advisable that no valuable files be placed on it, since we have to completely format the flash drive. The next component we need is a Windows OS distribution. Let it be the 64-bit version of Windows 7. Another feature of UEFI that should be mentioned is that this system does not support 32-bit operating systems from Microsoft.
Preparing a flash drive
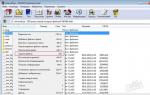
If we have the marked components, then we can start working. First, insert the USB flash drive. Then, open the command line in the Windows interface. It is necessary, however, that the user have administrator rights. Through you need to launch the DISKPART program - simply by entering this word. After this, you need to enter the list disk command, which will display a list of disks present in the system. You need to find a USB flash drive in it. If it is number 2 in the list, then you need to enter the command select disk 2.
Formatting a flash drive
Next you need to format the media. To do this, you need to enter the clean command. After this, you need to create a primary partition on the disk. This can be done using the create partition primary command. After this, the created partition should be made active. To do this, enter the active command. After this, you can display a list of sections. To do this, enter list volume in the command line. We find the section that we created. If it is listed as number 3, then enter the command select volume 3. After this, you need to format it in the FAT32 system. To do this, enter the command format fs=fat32. The basic bootable media is thus ready. But that is not all. You need to assign a drive letter to the flash drive. This can be done using the assign command. After that, enter exit and exit the command line.
Burning the distribution to a flash drive
After all the steps described above, you need to copy the Windows 7 distribution to a USB flash drive. This can also be done using the command line. How? There is a special command for this - xcopy. You need to enter it, then specify the address of the disk with the distribution kit, insert the * symbol, indicate the letter that corresponds to the flash drive intended for loading into UEFI, and then enter the command with the symbols /s /e. Then you need to go through the command line to the flash drive. There you need to go to the efi\microsoft\boot directory. It needs to be copied to the efi\boot folder. After this, you need to copy the file called bootmgfw.efi to the efi\boot folder, and then rename it to the bootx64.efi file.
The work with the flash drive is completed. A UEFI disk with the FAT32 file system, which we can just recognize without problems. Accordingly, you can install Windows 7 on a PC from it. Of course, provided that the Secure Boot algorithm is disabled in the UEFI options, which prohibits the installation of OSes that differ from Windows 8 on the computer.
Current Windows 8.1 And Win10 before its predecessor Win7 there are many advantages, one of them is working with hard GPT
-disks. GPT- this is a relatively new style of partitioning, the OS loads faster from such disks, they are more flexible to the data recovery procedure, and they can use the entire amount of disk space, if there is more of it 2.2 TB. Mandatory conditions for using benefits GPT
: BIOS UEFI on computer, versions only Win8.1 And Win10, and only them 64
-bit releases.
The first and last conditions are a given and cannot be circumvented. But with Windows versions it’s not so tough. On GPT -disk in principle you can install the edition x64 "Sevens", however, not without nuances. Below we will talk about these nuances, and also look at the universal installation method Win7 to disk GPT , which will be applicable in most cases, as long as computers have BIOS UEFI. Or at least a hybrid BIOS with the support EFI software regarding loading from GPT -disks.
1. Win7 on GPT disks: nuances
To Win7 successfully installed on GPT -disk, in BIOS UEFI must be disabled Secure Boot – a function that blocks the device from starting from any uncertified software. Which, in fact, is the Windows 7 distribution.
If "Seven" install on an empty, not yet partitioned and not initialized hard drive in compatibility mode BIOS UEFI c Legacy, during installation the system will automatically create MBR -disk. And it is on him that the system will be installed. However, if in BIOS set strict parameters UEFI– only this mode of operation, while booting from a flash drive UEFI, in some cases installation Win7 on an empty disk can go exactly the same way as if we were installing system versions 8.1 And 10 . During this installation, the system itself will initialize the disk as GPT and will create the necessary for EFI - systems technical sections. And later when reinstalling "Seven" will stand on without any problems GPT - a disk with an existing partition scheme. But we are talking about only a part of the cases.
The key points in all this are the correct parameters BIOS UEFI and flash drive UEFI with installation process Win7. And if in the latter case there is a universal way out of the situation in the form of recording programs UEFI -flash drive, then in the case of settings BIOS UEFI There cannot be a solution suitable for everyone a priori. Here, of course, you need to understand each PC and laptop separately. However, install "Seven" on GPT -disk can be done without interfering with the settings BIOS, if only there instead UEFI or compatibility mode is intentionally not enabled in normal mode BIOS - Legacy. This option exists in the form of an alternative Windows installation mechanism, which is offered by the program. This alternative can also be used in case of implementation on motherboards of incomplete BIOS UEFI, and hybrid firmware compatible with EFI only in terms of support for downloading from GPT -disks and installation DVD, but does not allow booting from UEFI -flash drive.
Below we consider two installation cases Win7 on GPT -disk:
First- when we are dealing with empty SSD or HDD
(or when the data stored on them is not valuable)
;
Second- when on GPT
- the disk already has markings, in particular, there are technical sections EFI
-Windows systems. This is an option without losing data stored on non-system partitions.
2. Bootable USB flash drive
To implement our plans, we will need a bootable flash drive with programs for working with disk partitioning. To do this, accordingly, it is necessary to prepare Live - a disk with all these tools on board. Perfect option - Live -disk WinPE10 TechAdmin. Its distribution in ISO The image can be downloaded for free here:
We write the downloaded image to a flash drive. To do this we use the utility Rufus. We indicate the flash drive in the first column, below we select the partition scheme - "GPT for UEFI computers". This is the mechanism for creating that same flash drive UEFI, which is fundamental for BIOS UEFI with selected mode only UEFI. If in BIOS Compatibility mode is present and active, you can select any scheme with a bootloader MBR . Then such a flash drive will become universal, and it will be possible to boot from it in Legacy on other PCs and laptops. Next we indicate the path to the image WinPE10 TechAdmin. And press "Start".

While the flash drive is being written, connect the installation ISO -image Win7 to display in Explorer.

Open the folder in the mounted drive "sources", and inside it we look for the file "install.wim"— installation WIM -image. As soon as the flash drive is written, copy it WIM -image and place it in the root of the flash drive.

This way we will have everything we need for installation on the flash drive. Win7. Indeed, in one of the methods described below, the disk on which the system will be installed will undergo repartitioning.

After placing it on a flash drive WIM - its weight will be approximately 5-6 GB. If it's a flash drive 8 GB, everything is fine. But if you only have a flash drive on 4 GB, after recording WinPE10 TechAdmin go to its root and delete the folder "AdminPE32" .

Now we look at the weight of the flash drive and figure out whether it will fit there WIM -image. If it still doesn’t fit, you can try to compress the image. Well, or download on the Internet an already compressed distribution kit with only the required edition "Sevens".
Boot from the newly created flash drive. Select download from .

3. Installing Win7 on an empty hard drive
So, the first installation method Win7 on GPT -disk is the case when we have either a clean SSD or HDD (without markings) , or when everything on them is not valuable and can be destroyed. On board WinPE10 TechAdmin launch the program.

Let's switch to the utility.

In the first tab "Physical disk" We indicate the desired disk, the one where we are going to install the OS. Next, click "Parts Management".

Then - .

In the window that appears, click the option "GUID". Next, check the options "Create ESP partition" And "Create MSR partition". Up in the block "Setting" remove values from the top three blocks. Click "OK" at the bottom. We confirm the actions.

Created a diagram of technical sections EFI -systems consisting of ESP -partition with file system FAT16 And MSR -section. Let's assign it to the first ESP - section letter, we will need this later. Press , select a letter in the new window, click "OK".

Thus, using We have created the necessary partitions for Windows, but the rest of the disk space can be distributed in a more usable way - with the help of any of those present on board WinPE10 TechAdmin disk managers.

Here's a whole section WITH can be divided into two or more sections.

After this we return to the program. In the first column of its window we indicate the path to WIM -image on a flash drive. In the second - choose ESP -the partition to which we gave the drive letter above, in the third - the partition itself Win7, i.e. future disk WITH . Below in the column we indicate the edition of the system. And press "Installation".

Next in the column we select "UEFI" on the right, on the left we make sure that the default value is set "Use BootSect...". If desired, activate auto-reboot upon completion of work . As a result, we press "OK".


Once this is complete, the computer will restart.

Now we need to boot from the disk where we just installed the OS. Next we will see the preparatory and configuration stages of installation.

4. Installing Win7 from a GPT disk with existing partitions
Installation "Sevens" for work GPT -disk - with existing markings, with technical sections EFI -systems (if you already had Win8.1 or Win10) , with data on other sections - it will be much easier. Here we need to run the program and, as in the previous case, specify:
Way to WIM-image,
Way to EFI-section;
Path to future disk WITH;
Editorial Win7, if the distribution provides several of them.

Where to get EFI-chapter? IN previous case using a section with the label has been created ESP. But Windows 8.1 And 10 during a normal installation, technical sections are created differently. It can be a diagram with two sections − EFI And MSR. Or maybe with three - EFI , MSR And WRE. In any case, we are only interested in the section EFI what's wrong with the file system? FAT32.

This is what needs to be indicated in the second column.
Specified program We format the sections. For the first EFI -partition, this is necessary so that the bootloader does not contain entries about non-existent operating systems. Finally, click .

We set the bootloader parameters and finally start the installation.

Developed more than 30 years ago, the basic BIOS input/output system is significantly outdated by modern standards. It is being replaced by the UEFI specification, which significantly changes the established and familiar boot procedure. This article is intended for those who are interested in installing Windows 7 on a computer with UEFI.
Replacement for outdated BIOS
Extensible Firmware Interface (extensible firmware interface) was developed by Intel in 1998. The current version of the specification is called Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. Computers manufactured after 2010 are highly likely to work with the UEFI system. Unlike BIOS, codes of the new specification can be stored both on the motherboard chip and in a special section of the HDD.
UEFI works with the new GPD partitioning, which is capable of supporting HDDs larger than 2 TB and an unlimited number of partitions. In addition, the UEFI architecture is modular and therefore supports custom applications and drivers. 
And, the most important part for this article: the new specification has a built-in download manager. Thanks to this, installing Windows 7 from USB or external HDD does not require third-party bootloaders.
Creating a bootable USB flash drive
To create a bootable flash drive, the Rufus 1.4.3 utility is considered. The program is notable for the fact that it does not require installation, is very small in size and is distributed completely free of charge. Of course, Rufus supports GPT HDD partitioning and work with the UEFI specification. The current version of the utility is available for download from the manufacturer's official website.

After launching the utility, you must specify the name of the flash drive that will be bootable ( Attention! All data from it will be permanently deleted!), file system (select FAT32), partition scheme and system interface (select GPT and UEFI). Opposite “create boot disk” you need to specify the path to the ISO image of Windows 7.
When all parameters are specified correctly, you can click on the “Start” button, and the process of preparing a bootable flash drive will begin. This will take some time, depending on the speed of your computer and the USB generation.
In addition to Rufus, you can use the WinSetupFromUSB program. It can also be downloaded from the manufacturer's website. The interface of these two programs is almost identical, so it makes no sense to consider the process of creating a bootable flash drive separately.
Installation Preparation
In order to start installation from a flash drive, you must first configure UEFI. To do this, you need to restart your computer and press F2 or Delete (depending on your motherboard, press both keys to be sure). After these steps, as in the case of the BIOS, you will be taken to the main control menu.
Press F7 or select the "Advanced" section. Next, go to the “boot” menu, select the “USB support” option and install Full Initialization. In the "secure boot" menu, set "Windows uefi mode".
Now open the Compatibility Support Module (or CSM) menu and in the “launch CSM” item select “enabled”. Open additional options and in the “boot device options” select “uefi only”. This item will allow you to filter flash drives and HDDs that cannot work with your specification. In the “boot from storage devices” column, select “both, uefi first”.
Now all you have to do is specify the boot priority. Place the bootable USB flash drive in the first place, and your HDD in the second. The settings are completed, save them with the F10 key, confirm the decision, and the computer will restart. 
Windows installation
If the previous steps were completed correctly, after the computer is rebooted, the standard installation of the operating system from the flash drive will begin. Click “next”, “install”, accept the user agreement, select full installation.

Now you need to open the command line using the combination Shift + F10. Next, enter the following sequence of commands:
diskpart (after each command you must press the enter button)
seldis 0
clean
convert gpt
exit
exit

More details at this point. Using these commands, you will delete all data from the HDD, mark it as GPD and format it for subsequent system installation. Click "update" and "next".
The installation of Windows 7 on the HDD of your personal computer will begin. During the installation process, the PC will be rebooted several times, after which you will only need to specify its name and password, time zone and set a list of users. Once the installation is complete, Microsoft Update will download and install all the necessary patches and drivers, and you can use your computer.