Hello, dear readers of the blog site. I would like to continue the topic of interpreting in simple words common terms that can be found everywhere in our computer age. A little earlier we already, as well as about and about.
Today we have a turn authentication. What does this word mean? Is this concept different from authorization or identification? What authentication methods are there, how secure are they, why can errors occur, and why is two-factor authentication better than one-factor authentication?
Interesting? Then let's continue, and I will try not to disappoint you.
What is authentication?
In fact, this is a procedure that is well known not only to us (modern residents), but also to our distant ancestors (almost from time immemorial).
To put it briefly, then authentication is the process of verifying authenticity(authenticity). And it doesn’t matter in what way (there are at least several types). The simplest example. You enter your apartment using the key to open the lock. And if the door does open, it means you have successfully passed authentication.
Let's break everything down in this example:
- The key to the lock is your identifier (inserted and turned - you are identified). In the computer world, this is analogous to the fact that you told the system yours.
- The process of opening (key and lock matching) is authentication. In the computer world, this is analogous to going through the authentication stage (verifying the entered password).
- Opening the door and entering the apartment is already authorization (gaining access). Online is an entrance to a site, service, program or application.
As you probably already understood, two-factor authentication in this example will be answered by the presence of a second lock on the door (or the presence of a dog in the house, which will already carry out its own authentication based on biometric signs - smell, appearance, presence of treats in your pocket) .
One more example. Stamp on a document (in a passport, wax seal on old letters).
As you can see, everything is extremely simple. But today this term is most often understood as electronic authentication, i.e. the process of logging into websites, services, systems, programs, and even connecting to your home WiFi network. But in essence, there are few differences from the example given.
In the electronic version, you will also have an identifier (in the simplest case) and a password (analogous to a lock) necessary for authentication (login to the system, gaining access to the Internet, logging into an online service, etc.).
As I said above, there is several types of authenticators:
As you can see, there is no ideal. Therefore, so-called two-factor (two-step) authentication is often used to enhance security. Let's look at an example.
Two-factor (2FA - two-step) authentication
For example, in and other services related to access to money, two-factor authentication comes down to the following:
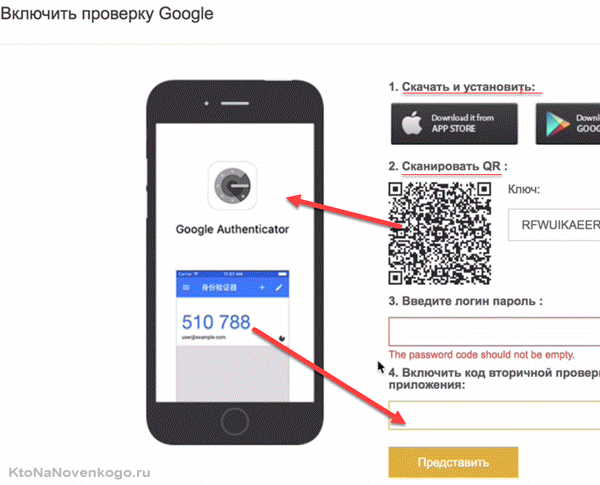
What does this give? Significantly improve security and reduce the risk of fraudsters authenticating for you. The fact is that intercepting a one-time password is much more difficult than finding out a multiple-use password. In addition, getting access to a mobile phone (and simply finding out its number) is much more difficult than digging through your computer or email.
But this is just one of examples of two-factor authentication (2FA). Let's take the bank cards already mentioned above. Here, too, two stages are used - authentication using the device (identification code on the card) and by entering a personal password (PIN code).
Another example from movies is when the access code is first entered, and then the retina or fingerprint is checked. In theory, you can do three stages, or four, or five. Everything is determined by the advisability of maintaining between heightened paranoia and a reasonable number of checks, which in some cases have to be done quite often.
In most cases, combining two factors is enough and does not cause very great inconvenience with frequent use.
Authentication errors
When using any of the types of authenticators mentioned above (passwords, devices, and biometrics), errors may occur. Where do they come from and how can they be avoided and resolved? Let's look at an example.
Let's say that you want to connect a computer or smartphone to the wireless network you have in your apartment. To do this, you will be required to enter the network name (identifier) and access password (authenticator). If everything is entered correctly, you will be authorized and you will have access to the Internet from the connected device.
But sometimes you may display an authentication error message. What should you do in this case?
- Well, first of all, check that the data you are entering is correct. Often, when entering, the password is closed with asterisks, which makes it difficult to understand the cause of the error.
- Passwords with characters in different cases (with capital and small letters) are often used, which not everyone takes into account when typing.
- Sometimes the error may be caused by a two-factor authentication system that is not entirely obvious. For example, the router may have access blocking enabled. In this case, the system checks not only whether the username and password are entered correctly, but also whether the Mac address of the device (from which you are logging in) matches the list of allowed addresses. In this case, you will have to go into the router settings (via a browser from a computer connected via Lan) and add the address of this device in the wireless network security settings.
Biometric systems can also produce recognition errors due to their imperfections or due to changes in your biometric data (hoarseness, swelling, numb eyes, cut finger). The same can happen with apps used for two-factor authentication. It is for these cases that a system for obtaining access using backup codes. Essentially, these are one-time passwords that will need to be printed and stored in a desk drawer (safe).
If you cannot authenticate using the usual method (an error is displayed), then backup codes will allow you to log in. For the next login you will need to use a new backup code. But this lifesaver also has the other side of the coin - if these backup codes are stolen or enticed (as happened to me), then they will work as a master key (universal master key) and all protection will go to waste.
Good luck to you! See you soon on the pages of the blog site
You can watch more videos by going to");">

You might be interested
Authentic - what is it, what does authenticity mean? Yandex Account - registration and how to use the service How to delete your page on Odnoklassniki  How to restore a page in Contact (if access is lost, deleted or blocked)
How to restore a page in Contact (if access is lost, deleted or blocked)  How to put a password on a folder (archive or otherwise password protect it in Windows) Why VK won’t load and the browser won’t log into VKontakte Identification - what is it and how is identity confirmed
How to put a password on a folder (archive or otherwise password protect it in Windows) Why VK won’t load and the browser won’t log into VKontakte Identification - what is it and how is identity confirmed