In this article we will talk about all possible ways run the cmd console with the highest rights in Windows 7, 8 and 10. Read about what this very launch as administrator means in ours.
Run Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 7
1 Press the button Start, in field Find programs and files enter cmd
2 Right-click on cmd.exe
3 Select:
Run Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 8.1
Method 1. The simplest:
- Click right click mouse on button Start;
- Click on:

Method 2
1 Open sidebar and select Search:

2 In the search field, enter cmd;
3 In the search results, find the item Command line and right-click on it;
4 Select Run as administrator

Running the console as administrator in Windows 10
The first method is fast, convenient and familiar since Windows 8.1:
- right click on the button Start;
- select Command Line (Administrator).

The second way is through the search bar on the taskbar.
- Enter cmd;
- Right-click on the search result;
- Select Run as administrator:

Running the CMD.exe file
1. Open the location of the cmd.exe file. It may be located in the following folders:
\Windows\System32\ \Windows\SysWOW64\
2. Right-click on the file and select Run as administrator:

Create a shortcut
You can create a shortcut to the cmd.exe file, where you select to run only as administrator:
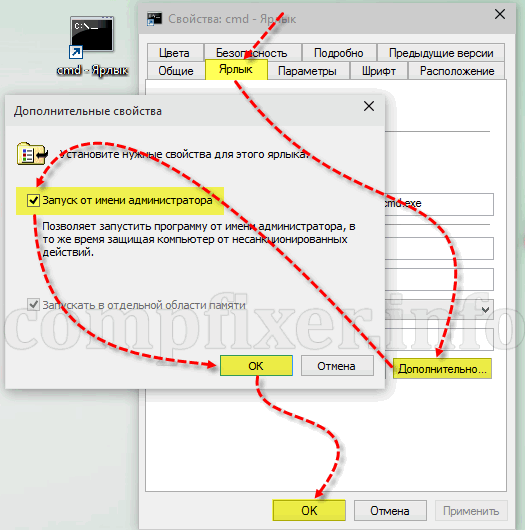
When you click on such a shortcut, a request for elevation will be issued and the console will start with the highest rights.
Some features
If current user No administrative rights on this computer, you will need to enter a password for any account, which has such rights, and click Yes:

If the command line is launched with administrator rights, then the title of the console window should read Administrator: Command line:

Which method do you prefer to use and why? Write in the comments.
Hi all! The author of this blog is with you again, and in this article I will tell you how to run the command line as an administrator. Perhaps someone will need it, so it won’t be superfluous. The article is short, so it won’t take much time. I'll give you a few launch examples. Go.
Method number 1. Create a shortcut to launch the command line
- Create a shortcut on your desktop. To do this, right-click on the desktop and select “Create” then “Shortcut”.
- You must enter the location of the object that will be launched. That is, the location command line. I suggest this option: %WinDir%\System32\cmd.exe or just enter cmd.
- Click Next.
- Enter a name for the shortcut. For example, “Command line” or “cmd”.
- Click on the shortcut RMB (right mouse button) and select “Properties”.
- In the window that opens, select the “Shortcut” tab and click on “Advanced...” in it. Then check the box as shown in the screenshot.

Method number 2. Launching the command line using the Start menu
Open the “Start” menu, then “All Programs” then “Accessories”. Next, right-click on the Command Prompt icon and click “Run as administrator.” Ready. This method will not work in Windows 10! It will start in normal mode.

Method No. 3. Using search in the start menu
Open the Start menu. Then enter the word "cmd". Then press the key combination Ctrl+Shift+Enter. The command line will start as administrator. Or click the right mouse button and context menu run as you need.

Method number 4. Launch using Explorer in Windows 8/10

Method No. 5. Launch using task manager
- Launch the task manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc or in the taskbar RMB).
- Next, click on “File” then “Run new task”. In the window that appears, enter “cmd” and check the box as shown in the screenshot.

Method number 6. Launch using the Shift button (without rights)
Go to your computer desktop or any other folder. Press the Shift key. Then click on the right mouse button to bring up the context menu. Next, select “Open Command Window.”
Sometimes for more fine tuning operating system or to use various “administrative” capabilities that are hidden from the eyes of ordinary users, you need to perform certain actions on the command line. Some of them can seriously affect the performance of the system, so they must be performed as a user with full rights.
How to Run Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows
The Windows interface has changed recently, which may cause an untrained user problems with launching certain applications if the sequence of actions is described for some other operating system. Therefore, we will show all the options in more detail.
How to start the command line in Windows XP and 7
One of the most simple options for XP: click “Start” – “Programs” – “Accessories” – “Command Prompt”.

Right-click on this icon and select "Run as administrator".
For the "seven" the following method is interesting: create a shortcut on the desktop - right-click - “Create” – “Shortcut”.
Enter cmd.exe in the field “Specify the location of the object”.

After the shortcut is created, you need to go into it with the right mouse button - Properties.

Then click on the “Advanced” button and check the “Run as administrator” checkbox.

Click "OK" to apply the changes.
Command Prompt and Administrator Rights in Windows 8 and 10
Due to the changed interface, the startup order is slightly different than in the systems described above. For Windows 8:
Go to the Start screen and type cmd - the search will find you the command line shortcut you need. Or find it manually - by right-clicking in an empty space home screen and selecting All apps.
 Right-click on it and a panel with action options will open at the bottom of the window. Select in it – Run as administrator.
Right-click on it and a panel with action options will open at the bottom of the window. Select in it – Run as administrator.

In the “ten” the following option is convenient:
Find Search on the taskbar or click the Start button. In the search bar or in the Start menu that opens, type cmd. Right-click on the found Command Prompt (Desktop) shortcut and select “Run as administrator.”

Before making changes to the system as an administrator, be careful and careful to prevent problems with the operation of the software.
– Igor (Administrator)
It's no secret that a number of Windows operating system applications require administrator rights. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to run the command Windows string with administrator rights. In this sense, in Windows system XP everything was quite simple. If you have administrator rights, then all applications you launch will have them. Those. you don't have to do anything. If you didn’t have rights, then you could run the application on behalf of another user (of course, knowing the password and login).
However, starting from Windows Vista and Windows 7, the situation has changed somewhat. The so-called UAC (User Account Control) appeared. The idea is really interesting. Limit ordinary users from many mistakes. But, unfortunately, the implementation of such an idea made the work of most experienced users very inconvenient. Too many actions were required from the user to configure the system so that the huge number of warnings did not appear. Luckily, UAC can be disabled.
Running Command Prompt with Administrator Rights in Windows Vista/7 in the Normal Way
- Right-click on "cmd" or "cmd.exe" in the list of programs.
- Select "Run as administrator"
- If a UAC warning window appears, click "Yes".
Run Command Prompt with Administrator Rights in Windows Vista/7 with Keyboard Shortcut
- Open the "Start" menu
- Enter "cmd" (without quotes) in the "Start Search" field (" Start search") (Vista) or "Search programs and files" (Win 7)
- Then press the key combination Ctrl + Shift + Enter (must be pressed simultaneously)
- If a UAC warning window appears, click "Yes". You can also use the keyboard shortcut Alt + C to confirm the action.
Create a shortcut to launch command line in Windows 7 / Vista with elevated privileges

If you use the command line frequently, it's best to create a shortcut once rather than using keyboard shortcuts or the context menu every time. Although, this is more a matter of habit. However, the shortcut also has its advantages. At a minimum, it can be placed on the panel quick launch, and then you only need one click to launch. So let's get started:
- Right-click on an empty area of your desktop
- Select "New" from the context menu
- Select "Shortcut"
- In the "Specify the location of the object" field, enter "cmd.exe" (without quotes)
- Click "Next". Give the shortcut a name, for example "cmd.exe", and click "Finish"
- Right-click on the created shortcut
- Select "Properties" from the context menu
- Click the "Advanced" button
- Check the box for “Run as administrator”
- Click "OK"
You now have a shortcut that will open a command prompt with administrator rights when double click. Well, or you can pin it to the quick launch panel, as mentioned earlier. Agree that it is convenient. Please note that if UAC is enabled, a warning window will still appear when you open the console.
Hi all. Guys, in this post I’ll tell you how to run cmd in Windows 7 with admin rights and I’ll also show a little trick how to do this whole thing with... a batch file. Yes, and I’ll tell you what a body file is. So, first, a little information, so to speak, introductory. If in simple words, then the command line is a black window where you can enter all sorts of commands that can help in setting up Windows. A batch file is a file in which these commands can be written; you can write several of them there and they will all be executed in turn. That is, a body file is something like a script.
You can do a lot of useful things in a body file, but you need to fumble around cmd commands. But the most interesting thing, in principle, it seems to me, is that it’s enough to understand one thing - to understand the cmd help, there is help for any command =)
ATTENTION!!! Guys, if you need to run a command as an administrator, then first you need to run the command line itself as an administrator! And in it all commands will be AUTOMATIC on behalf of the administrator! I wrote about it here!
Guys, I’ll say right away that the task with the batch file failed, I’m talking about launching the batch file with admin rights. I thought it was simple, but it turned out that it was kind of unrealistic...
So you press Win + R, but paste this:
C:\Windows\System32

Then a folder will open, you write cmd there in the upper right corner, then wait a little and the result will appear immediately:

And now you just need to right-click cmd and select run as administrator:

And that’s it, then the command line will start and there should be the word Administrator in the title:

So, I also promised to show how to launch this command line as an administrator using a batch file. Hmm, this is a tricky one, but look, first let’s create a batch file called cmd_admin.bat, I’ll create it on the desktop:

Do you know how to create a body file? Right-click on the desktop, then create Text Document. Its name, that is, New text document.txt, is completely changed to the name of the batch file, in our case it is cmd_admin.bat, everything is simple. If you don’t see the extension, that is, the last thing in the name that comes after the dot, well, I mean .txt or .bat, then you need to enable the display of file extensions. To do this, go to the control panel, find the Folder Options icon and there, on the View tab at the very bottom, uncheck this box:

I think it’s clear =) So, we have created a body file, what next? Right-click on it and select Edit:

And an empty batch file will open:

So guys.. I have bad news for you, unfortunately, it seems like it’s impossible.. I thought it was possible, but it turns out it’s not. All I found was this command:
runas /savecred /user:"Administrator" cmd.exe
Or this one:
runas /savecred /user:administrator "cmd.exe"
I inserted the second one into the batch file, launched it, but it requires a password:

I don’t even know what password we’re talking about... No, well, you can run a batch file like this (but I think that’s not what you meant):

And if you write cmd in the batch file itself, then the command line will be launched as administrator .. but this is not the same, I know.. No, well, you can also go to the properties of the batch file and there, on the Compatibility tab, put a checkmark at the bottom to run only from admin.. but that’s not it.. =(
Guys, sorry, but.. alas.. I'm talking about the body file. True, there is still not very good news - if you think logically .. then it seems impossible without third-party modules, if on a pure batch file, without VBS, then I think it can’t be done and all because that’s how security works =(Good luck to you , sorry it didn’t work out, but don’t be sad... see you friends!