simple circuit color music on 220V lamps
Everyone knows and almost everyone assembles this device that flickers and blinks to the music - color music. On the Internet, many search for color music schemes using various queries and they are different everywhere. I present to your attention the diagram below appearance which you see in the pictures. And so, circuit of working color music for 220 Volts on teristors
A simple color scheme
 It will require the bare minimum of parts.
It will require the bare minimum of parts.
We buy colored incandescent lamps 220V
Considering that the output stage of the color music is made of thyristors, it has high power. If thyristors are placed on heat sinks, then each channel can be loaded with 1000 watts. But for a home, 60-100 watt lamps are quite enough.

Drawing of a printed circuit board for light and music

I did not use laser-iron technology for such a simple board design. I simply printed the image as a mirror image and placed it on the foil.

To prevent the paper from moving, we secure it with tape or something else and mark the places of future holes

We paint the tracks themselves with nitro paint

Any transformer from a Chinese power supply, whether from a radiotelephone or something else, will be suitable as a transformer.
And look at the completely soldered board

We attach the cartridges to the aluminum corner

In addition to the photo sent
The inexhaustible potential of LEDs has once again been revealed in the design of new and modernization of existing color and music consoles. 30 years ago, color music, assembled from multi-colored 220-volt light bulbs connected to a cassette recorder, was considered the height of fashion. Now the situation has changed and the function of a tape recorder is now performed by any multimedia device, and instead of incandescent lamps, super-bright LEDs or LED strips are installed.
The advantages of LEDs over light bulbs in color music consoles are undeniable:
- wide color gamut and more saturated light;
- various design options (discrete elements, modules, RGB strips, rulers);
- high response speed;
- low power consumption.
How to make color music using a simple electronic circuit and make the LEDs blink from the source audio frequency? What are the conversion options? sound signal exist? Let's look at these and other questions using specific examples.
The simplest circuit with one LED
First you need to understand a simple color music scheme assembled on one bipolar transistor, resistor and LED. It can be powered from a DC source with a voltage of 6 to 12 volts. This color music works on one transistor according to the principle of an amplification stage with a common emitter. A disturbing influence in the form of a signal with varying frequency and amplitude arrives at the VT1 base. As soon as the oscillation amplitude exceeds a certain threshold value, the transistor opens and the LED flashes.
The disadvantage of this simplest scheme is that the rate of blinking of the LED depends entirely on the level of the sound signal. In other words, a full-fledged color-musical effect will be observed only at one volume level. Lowering the volume will result in a rare wink, while increasing the volume will result in an almost constant glow.
Scheme with single-color LED strip
The simplest color music on a transistor above can be assembled using LED strip under load. To do this, you need to increase the supply voltage to 12V, select a transistor with the highest collector current exceeding the load current and recalculate the resistor value. This simple color music from an LED strip is perfect for beginning radio amateurs to assemble with their own hands, even at home.
Simple three-channel circuit
A three-channel audio converter allows you to get rid of the shortcomings of the previous scheme. The simplest scheme of color music with the division of the sound range into three parts is shown in the figure.  It is powered by a constant voltage of 9V and can illuminate one or two LEDs in each channel. The circuit consists of three independent amplifier stages assembled on KT315 (KT3102) transistors, the load of which includes LEDs of different colors. As a pre-amplification element, you can use a small step-down network transformer.
It is powered by a constant voltage of 9V and can illuminate one or two LEDs in each channel. The circuit consists of three independent amplifier stages assembled on KT315 (KT3102) transistors, the load of which includes LEDs of different colors. As a pre-amplification element, you can use a small step-down network transformer.
The input signal is fed to the secondary winding of the transformer, which performs two functions: galvanically isolates the two devices and amplifies the sound from the line output. Next, the signal goes to three parallel-connected filters assembled on the basis of RC circuits. Each of them operates in a specific frequency band, which depends on the values of resistors and capacitors. The low-pass filter passes sound vibrations with a frequency of up to 300 Hz, as indicated by the blinking red LED. Sound in the range of 300-6000 Hz passes through the mid-pass filter, which is manifested in the flickering of the blue LED. The high-pass filter passes a signal whose frequency is greater than 6000 Hz, which corresponds to the green LED. Each filter is equipped with a trimming resistor. With their help, you can set the uniform glow of all LEDs, regardless of the musical genre. At the output of the circuit, all three filtered signals are amplified by transistors.
If the circuit is powered from a low-voltage DC source, then the transformer can be safely replaced with a single-stage transistor amplifier.  Firstly, galvanic isolation loses its practical meaning. Secondly, the transformer is several times inferior to the circuit shown in the figure in terms of weight, size and cost. The circuit of a simple audio amplifier consists of a KT3102 transistor, two capacitors that cut off the DC component, and resistors that provide the transistor with a common emitter. Using a trimmer resistor, you can achieve overall amplification of a weak input signal.
Firstly, galvanic isolation loses its practical meaning. Secondly, the transformer is several times inferior to the circuit shown in the figure in terms of weight, size and cost. The circuit of a simple audio amplifier consists of a KT3102 transistor, two capacitors that cut off the DC component, and resistors that provide the transistor with a common emitter. Using a trimmer resistor, you can achieve overall amplification of a weak input signal.
In the case when it is necessary to amplify the signal from the microphone, connect to the input of the previous circuit electret microphone, applying potential to it from the power source. Two-stage circuit preamplifier shown in the figure.  In this case, the trimming resistor is located at the output of the first amplifier stage, which gives more opportunities for adjusting sensitivity. Capacitors C1-C3 pass the useful component and cut off D.C.. Any electret microphone is suitable for implementation; for normal operation, a bias of 1.5 V is sufficient.
In this case, the trimming resistor is located at the output of the first amplifier stage, which gives more opportunities for adjusting sensitivity. Capacitors C1-C3 pass the useful component and cut off D.C.. Any electret microphone is suitable for implementation; for normal operation, a bias of 1.5 V is sufficient.
Color music with RGB LED strip
The following circuit of a color music console operates on 12 volts and can be installed in a car. It combines the main functions of the previously discussed circuit solutions and is capable of operating in color music and lamp modes.
The first mode is achieved through contactless control of the RGB strip using a microphone, and the second mode is achieved through the simultaneous illumination of red, green and blue LEDs on full power. The mode is selected using a switch located on the board. Now let's take a closer look at how to make color music that is perfect even for installation in a car, and what parts are required for this.
Structural scheme
To understand how this color music console works, let’s first look at it block diagram. It will help trace the full path of the signal.  The source of the electrical signal is a microphone, which converts sound vibrations from the phonogram. Because This signal is too small and must be amplified using a transistor or operational amplifier. Next comes the automatic level controller (AGC), which keeps the sound fluctuations within reasonable limits and prepares it for further processing. Filters divide the signal into three components, each of which works in only one frequency range. In the end, all that remains is to amplify the prepared current signal, for which transistors operating in switching mode are used.
The source of the electrical signal is a microphone, which converts sound vibrations from the phonogram. Because This signal is too small and must be amplified using a transistor or operational amplifier. Next comes the automatic level controller (AGC), which keeps the sound fluctuations within reasonable limits and prepares it for further processing. Filters divide the signal into three components, each of which works in only one frequency range. In the end, all that remains is to amplify the prepared current signal, for which transistors operating in switching mode are used.
Schematic diagram
Based on the structural blocks, we can proceed to a consideration of the circuit diagram. Its general appearance is shown in the figure.  To limit current consumption and stabilize the supply voltage, resistor R12 and capacitor C9 are installed. R1, R2, C1 are set to set the microphone bias voltage. Capacitor C fc is selected individually to specific model microphone during setup. It is needed in order to slightly muffle the signal of the frequency that prevails in the microphone’s operation. Usually the influence of the high-frequency component is reduced.
To limit current consumption and stabilize the supply voltage, resistor R12 and capacitor C9 are installed. R1, R2, C1 are set to set the microphone bias voltage. Capacitor C fc is selected individually to specific model microphone during setup. It is needed in order to slightly muffle the signal of the frequency that prevails in the microphone’s operation. Usually the influence of the high-frequency component is reduced.
Unstable voltage in the vehicle network can affect the operation of color music. Therefore, it is most correct to connect homemade electronic devices through a 12V stabilizer.
Sound vibrations in the microphone are converted into an electrical signal and, through C2, are supplied to the direct input of the operational amplifier DA1.1. from its output the signal goes to the input of the operational amplifier DA1.2, equipped with a circuit feedback. The resistances of resistors R5, R6 and R10, R11 set the gain DA1.1, DA1.2 equal to 11. The elements of the OS circuit: VD1, VD2, C4, C5, R8, R9 and VT1, together with DA1.2, are part of the AGC. At the moment a signal of too large an amplitude appears at the output of DA1.2, transistor VT1 opens and, through C4, closes the input signal to the common wire. This results in an instantaneous reduction in the output voltage.
Then stabilized alternating current The audio frequency passes through the cut-off capacitor C8, after which it is divided into three RC filters: R13, C10 (LF), R14, C11, C12 (MF), R15, C13 (HF). In order for the color music on LEDs to shine brightly enough, you need to increase the output current to corresponding value. For tape with a consumption of up to 0.5A per channel, medium-power transistors such as KT817 or imported BD139 without mounting on a radiator are suitable. If the do-it-yourself light-music assembly involves a load of about 1A, then the transistors will require forced cooling.
In the collectors of each output transistor (parallel to the output) there are diodes D6-D8, the cathodes of which are connected to each other and connected to switch SA1 (White light). The second contact of the switch is connected to the common wire (GND). While SA1 is open, the circuit operates in color music mode. When the switch contacts are closed, all the LEDs in the strip light up at full brightness, forming a total white stream of light.
Printed circuit board and assembly parts
To make a printed circuit board, you will need a single-sided PCB measuring 50 by 90 mm and a ready-made .lay file, which can be downloaded. For clarity, the board is shown from the side of the radio elements. Before printing, you must set its mirror image. Layer M1 shows 3 jumpers placed on the parts side.  To assemble color music from an LED strip with your own hands, you will need accessible and inexpensive components. An electret type microphone, suitable in a protective case from old audio equipment. Light music is assembled on a TL072 chip in a DIP8 package. Capacitors, regardless of type, must have a voltage reserve and be designed for 16V or 25V. If necessary, the board design allows you to install output transistors on small radiators. A terminal block with 6 positions is soldered on the edge for supplying power, connecting an RGB LED strip and a switch. A complete list of elements is given in the table.
To assemble color music from an LED strip with your own hands, you will need accessible and inexpensive components. An electret type microphone, suitable in a protective case from old audio equipment. Light music is assembled on a TL072 chip in a DIP8 package. Capacitors, regardless of type, must have a voltage reserve and be designed for 16V or 25V. If necessary, the board design allows you to install output transistors on small radiators. A terminal block with 6 positions is soldered on the edge for supplying power, connecting an RGB LED strip and a switch. A complete list of elements is given in the table.  In conclusion, I would like to note that the number of output channels in a homemade color music set-top box can be increased as many times as desired. To do this, you need to divide the entire frequency range into a larger number of sectors and recalculate the bandwidth of each RC filter. Connect LEDs of intermediate colors to the outputs of additional amplifiers: violet, turquoise, orange. Do-it-yourself color music will only become more beautiful from such an improvement.
In conclusion, I would like to note that the number of output channels in a homemade color music set-top box can be increased as many times as desired. To do this, you need to divide the entire frequency range into a larger number of sectors and recalculate the bandwidth of each RC filter. Connect LEDs of intermediate colors to the outputs of additional amplifiers: violet, turquoise, orange. Do-it-yourself color music will only become more beautiful from such an improvement.
The given diagrams belong to the site cxem.net
Read also
Almost every novice radio amateur, and not only others, had a desire assemble a color music console or running fire to add variety to your music listening in the evening or at holidays. In this article we will talk about a simple color music console assembled on LEDs, which even a novice radio amateur can assemble.
1. The operating principle of color music consoles.
Operation of color music consoles ( CMP, CMU or SDU) is based on frequency division of the spectrum of an audio signal with its subsequent transmission through separate channels low, average And high frequencies, where each channel controls its own light source, the brightness of which is determined by the vibrations of the sound signal. The end result of the console's operation is to receive color range corresponding to the piece of music being played.
To obtain a full gamut of colors and the maximum number of color shades, color music consoles use at least three colors:

The frequency spectrum of the audio signal is divided using LC- And RC filters, where each filter is tuned to its own relatively narrow frequency band and passes through only the vibrations of this part of the audio range:
1
. Low pass filter(low-pass filter) transmits vibrations with a frequency of up to 300 Hz and the color of its light source is chosen red;
2
. Mid Pass Filter(PSC) transmits 250 – 2500 Hz and the color of its light source is chosen green or yellow;
3
. Filter higher frequencies
(HPF) transmits from 2500 Hz and above, and the color of its light source is chosen blue.

There are no fundamental rules for choosing the bandwidth or color of the lamps, so each radio amateur can use colors based on the characteristics of his perception of color, and also change the number of channels and frequency bandwidth at his own discretion.
2. Schematic diagram of a color music console.
The figure below shows a diagram of a simple four-channel color and music set-top box assembled using LEDs. The set-top box consists of an input signal amplifier, four channels and a power supply that supplies the set-top box with AC power.

The audio frequency signal is supplied to the contacts PC, OK And General connector X1, and through resistors R1 And R2 goes to the variable resistor R3, which is a regulator of the input signal level. From the middle terminal of the variable resistor R3 sound signal through a capacitor C1 and resistor R4 goes to the input of a pre-amplifier assembled on transistors VT1 And VT2. The use of an amplifier made it possible to use the set-top box with almost any audio source.
From the output of the amplifier, the audio signal is supplied to the upper terminals of trimming resistors R7,R10, R14, R18, which are the load of the amplifier and perform the function of adjusting (tuning) the input signal separately for each channel, and also set the desired brightness of the channel LEDs. From the middle terminals of the trimming resistors, the audio signal is supplied to the inputs of four channels, each of which operates in its own audio range. Schematically, all channels are designed identically and differ only in RC filters.
Per channel higher R7.
The channel bandpass filter is formed by a capacitor C2 and passes only the high-frequency spectrum of the audio signal. Low and medium frequencies do not pass through the filter, since the capacitor resistance for these frequencies is high.
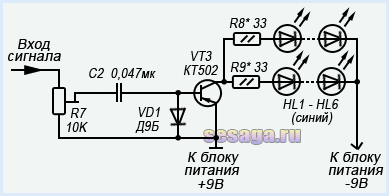
Passing the capacitor, the high-frequency signal is detected by a diode VD1 and is fed to the base of the transistor VT3. The negative voltage appearing at the base of the transistor opens it, and a group of blue LEDs HL1 — HL6 included in its collector circuit are ignited. And the greater the amplitude of the input signal, the stronger the transistor opens, the brighter the LEDs burn. To limit the maximum current through the LEDs, resistors are connected in series with them R8 And R9. If these resistors are missing, the LEDs may fail.
Per channel average frequency signal is supplied from the middle terminal of the resistor R10.
The channel bandpass filter is formed by a circuit С3R11С4, which exhibits significant resistance for low and higher frequencies, therefore, to the base of the transistor VT4 Only mid-frequency oscillations are received. LEDs are included in the collector circuit of the transistor HL7 – HL12 Green colour.
Per channel low frequency signal is supplied from the middle terminal of the resistor R18.
The channel filter is formed by a circuit С6R19С7, which attenuates signals of medium and high frequencies and therefore to the base of the transistor VT6 Only low frequency vibrations are received. The channel load is LEDs HL19 – HL24 Red.
For a variety of colors, a channel has been added to the color music console yellow colors. The channel filter is formed by a circuit R15C5 and operates in the frequency range closer to low frequencies. The input signal to the filter comes from a resistor R14.
The color music console is powered by constant voltage 9V. The power supply unit of the set-top box consists of a transformer T1, diode bridge made on diodes VD5 – VD8, microcircuit voltage stabilizer DA1 type KREN5, resistor R22 and two oxide capacitors C8 And C9.
The alternating voltage rectified by the diode bridge is smoothed by an oxide capacitor C8 and goes to the voltage stabilizer KREN5. From the output 3 microcircuit, a stabilized voltage of 9V is supplied to the set-top box circuit.
To obtain an output voltage of 9V between the negative bus of the power supply and the output 2 chip included resistor R22. By changing the resistance value of this resistor, the desired output voltage is achieved at the pin 3 microcircuits.
3. Details.
The set-top box can use any fixed resistors with a power of 0.25 - 0.125 W. The figure below shows resistor values that use colored stripes to indicate the resistance value:

Variable resistor R3 and tuning resistors R7, R10, R14, R18 of any type, as long as they fit the size of the printed circuit board. In the author's version of the design, a domestic variable resistor of the SP3-4VM type and imported trimming resistors were used.

Permanent capacitors can be of any type, and are designed for an operating voltage of at least 16 V. If difficulties arise in purchasing a C7 capacitor with a capacity of 0.3 μF, it can be composed of two connected in parallel with a capacity of 0.22 μF and 0.1 μF.
Oxide capacitors C1 and C6 must have an operating voltage of at least 10 V, capacitor C9 not below 16 V, and capacitor C8 not below 25 V.

Oxide capacitors C1, C6, C8 and C9 have polarity, therefore, when mounting on a breadboard or printed circuit board this must be taken into account: for Soviet-made capacitors, the positive terminal is indicated on the case; for modern domestic and imported capacitors, the negative terminal is indicated.

Diodes VD1 – VD4 any from the D9 series. A colored stripe is applied to the diode body on the anode side, identifying the letter of the diode.

As a rectifier assembled on diodes VD5 - VD8, a ready-made miniature diode bridge, designed for a voltage of 50V and a current of at least 200 mA.

If you use rectifier diodes instead of a ready-made bridge, you will have to slightly adjust the printed circuit board, or even move the diode bridge outside the main board of the set-top box and assemble it on a separate small board.
For self-assembly of the bridge, the diodes are taken with the same parameters as the factory bridge. Any rectifier diodes from the KD105, KD106, KD208, KD209, KD221, D229, KD204, KD205, 1N4001 - 1N4007 series are also suitable. If you use diodes from the KD209 or 1N4001 - 1N4007 series, then the bridge can be assembled directly from the printed circuit board directly on the contact pads of the board.
LEDs are standard with yellow, red, blue and green colors. Each channel uses 6 pieces:

Transistors VT1 and VT2 from the KT361 series with any letter index.

Transistors VT3, VT4, VT5, VT6 from the KT502 series with any letter index.

Voltage stabilizer type KREN5A with any letter index (imported analogue 7805). If you use nine-volt KREN8A or KREN8G (imported analogue 7809), then resistor R22 is not installed. Instead of a resistor, a jumper is installed on the board, which will connect the middle pin of the microcircuit to the negative bus, or this resistor is not provided at all during the manufacture of the board.

To connect the set-top box to the sound source, a three-pin jack connector is used. The cable is taken from a computer mouse.

Power transformer - ready or homemade power at least 5 W with a voltage on the secondary winding of 12 - 15 V at a load current of 200 mA.
In addition to the article, watch the first part of the video, which shows the initial stage of assembling a color music console
This ends the first part.
If you are tempted make color music using LEDs, then select the parts and be sure to check the serviceability of diodes and transistors, for example. And we will carry out the final assembly and configuration of the color and music console.
Good luck!
Literature:
1. I. Andrianov “Attacks for radio receivers.”
2. Radio 1990 No. 8, B. Sergeev “Simple color and music consoles.”
3. Operating manual for the “Start” radio designer.
Homemade color music
Homemade color music in the interior of your own car will be of interest to all lovers of beautiful disco music. Making it with your own hands is absolutely easy.
Color music at home can be quickly and easily assembled if you know some of the nuances of the circuit and its correct installation.
Color music schemes in cars
A large number of homemade color music schemes are published on amateur radio forums. Some of them are intended only for experienced, others for beginners.
In principle, all circuits are built according to the same principle, which is recommended to be understood so that the assembly no longer represents something impracticable and very complex.
Simple scheme
Even a schoolchild can assemble color music using this scheme, because it consists of only one transistor. Its name is KT815G.
This color music can be assembled using diodes borrowed from a simple flashlight.
Everything is done as follows:
- We divide the LEDs that we removed from the flashlight in half;
- We find a suitable box in which we will assemble our circuit. In this case, instead of a box, a rectangular plastic box from used shoe polish is ideal;
- We take out the switch. It will change the light-music mode to simple lighting.
Note. The LEDs will flash with bass and the higher the volume, the brighter they glow. As for the channels, two are enough, not connected to the speaker.
- The power source in our case will be three AA batteries;
- All that remains is to put the homemade color music in the trunk and enjoy the effect.
Complex circuits
They will allow you to create more professional schemes from the user's point of view.
First version of the scheme
It is assembled on five diodes. All of them are five millimeter and 3 V, have clear lenses. The transistor used is KT815 or KT972. Its task is to strengthen and act as a key.
Everything is done like this:
- Power is supplied from 2 1.5-volt batteries;
- There are respectively two inputs for music: X1 and X2;
- In place of LED3 we install a red diode, the remaining remaining pairs will be blue and green;
Note. As a result, we get a very successful color and music scheme. The LEDs glow very effectively to the beat of the music, the circuit consumes little current, and low frequencies They play just great. You just need to be careful: the LEDs may not be able to withstand loud music and burn out.
Second version of the scheme
We find the KT817 transistor, wires, headphone plug and SD tape.
Started:
- We solder the transistor according to the following scheme;
- Then the CD tape is added and everything is moved to the luggage compartment of the car.
Light music from garlands
A completely successful solution that will require the use of light bulbs from New Year's garlands:
- Garlands (see) need to be collected together in several pieces and secured with electrical tape;
- Make an adapter to connect to the head unit and connect the wire.
Note. The circuit in this case will involve eight twisted pair conductors, which transmit the signal from the contacts of the control unit to the color music control unit.
Color music from LEDs
An original scheme for making beautiful color music. In this case, you need a housing made of plexiglass.
Let's get started:
- We select two plates measuring 5x15 cm and two square plates 5x5 cm;
- A couple of holes are made in one of the parts (for power supply and headphones);
- We mat and sand all the plates;
- We find LEDs that we also matte for a better effect;
- We assemble the body using a heat gun, which is ideal for working with plexiglass;
- Now we assemble the electrical circuit for color music according to this diagram:
- We connect the wire from the headphones with the corresponding connector to the car radio and enjoy the effect.
The plexiglass case can be installed in the car interior, anywhere. Everything will depend on individual preferences, wire length, etc.
During the work process, the following must be taken into account:
- The output voltage of the adapter and the rated voltage of each diode must be interconnected. In other words, the total number of diodes involved in the circuit must equal the ratio of the adapter's output voltage.
Note. As an example, if the adapter is 12V, and the voltage for each diode is 3V, then the total number of LEDs should be 4.
- It is advisable to use a 3-core wire, one of the wires of which should be left unused.
Circuit with signal from speaker
Another popular scheme for creating color music.
We do the following:
- We take the signal from the speakers (see).
Note. In this case, it is very important not to short-circuit the output of the SPD*. For this purpose, we solder only one wire.
UZP* - Sound card amplifier
- Arranges the switch so that it turns on the LEDs based on music;
- We select the resistance according to the diagram below, where the rating for turning on one diode is indicated;
Note. If the color music will be assembled from 4 LEDs, then the R value should be equal to 820 Ohms.
Popular multi-color scheme
Another common scheme involves the possibility of increasing nutrition. This will be especially true if a chain of many LEDs is used.
The scheme is like this:
- There should be two frequency filters. They allow HF and LF to pass through at the input;
- The signal then goes to the amplifier stages, and then to the LEDs;
- It is recommended to connect inputs 1 and 2 to the source speaker.
Advice. If you want to make color music brighter, then you just need to reduce the resistor values to a couple of hundred, and change the transistors to KT817.
This scheme has one advantage that no other has: the ability to use LEDs of any color.
So, when playing low-frequency bass, the red LED will blink, while playing midrange and high-frequency – green. As for setting the brightness, it is regulated by the sound volume rotary: the higher the sound, the brighter the glow.
Car ceiling in LEDs
If you wish, you can not only arrange something similar to a disco in the car, but also build a backlight that would either turn on separately or be connected with music playback. This operation also involves the use of LEDs.
“Starry sky” on the ceiling of the car will look wonderful. This type of lighting, it turns out, has been practiced for a long time, and not only in cars, but also in our own apartments.
This scheme can be used in different ways:
- Place the LEDs evenly, in any shape or like a certain figure;
- Use light bulbs of different luminous power to imitate the glow of stars (bright/not bright);
- Use different ceiling backgrounds. For example, you can drag it black.
Creation instructions:
- We drag the ceiling of the car;
- We assemble or purchase a current stabilizer.
Note. Very important on at this stage do everything right. Otherwise, you will have to dismantle the assembled ceiling if the diodes burn out. To avoid this situation, you need to check the circuit after assembly (find out how many volts and how much current the circuit has). As test block An old power supply from a computer will do.
- We use a large capacitor to smoothly dim the LEDs. Suitable, for example, KT470;
- Place the diagram in a matchbox;
- We check the operation by connecting three LEDs and one resistor in series;
- On the ceiling, we insert LEDs into the holes, which are fixed on the back side with glue;
- We also attach the switch and stabilizer.
Note. The LEDs can be grouped in groups of 3 and connected to a resistor, and then the groups can be routed to the stabilizer in parallel.
That's all. We hope that the reader will be able to choose something for himself from the given diagrams. Just remember to take care not to turn on beautiful color music while the car is moving. This greatly distracts you from the road and can cause an accident.
In the process of working with your own hands, a video review on the topic, photos - materials, diagrams, etc. will be useful. Instructions similar to those given above can be found in other articles on our site. The price of independently creating and installing color music is considered the lowest in the world of auto tuning, because Consumables You can also make it yourself.