The goals pursued are safety and safety again.
Let's imagine a very common situation: you have many servers on your network that provide some services. It is very likely that some of them have front end, which looks into the WAN, i.e. V global network. Usually this is a Proxy server, Web server, mail server, etc. It's no secret that this fact itself makes you think about how literate system administrator about the security of your network infrastructure. It makes no sense to tell you what could happen if a hacker penetrates your network. There are many options to protect yourself from malicious attacks. Among them is building a so-called demilitarized zone or publishing a server through your proxy, which you certainly (isn’t it?) configured very strictly and seriously. The first option (DMZ) has not yet been “raised” due to some reasons. Let it be a lack of time and equipment for the system administrator. The second one (publish through another server) is very controversial, we’ll leave it out for now. For now, first, let's set up a firewall, also known as a firewall, or firewall. The main function of any firewall is to secure access to our computer from the outside. I specifically wrote the word “computer” because home computers and workstations can also be secured using a screen. Naturally, there is no 100% protection with a software firewall, but it’s better than nothing. In addition, I have a feeling that after my manipulations today, the server will no longer be at risk. Let's get started.
Laboratory stand
There is a server based Windows Server 2008 R2, which provides VPN service using the Microsoft RAS service. Windows Firewall is configured by default. I didn’t delve into it, although I should have. But because you have a corporate license for Kaspersky Enterprise Space Security, why not take advantage of it and install Kaspersky Endpoint Security 8, which includes a software firewall.
Configuring Kaspersky firewall
The Kaspersky Endpoint Security 8 firewall is identical to many screens from this manufacturer, including home version Kaspersky Internet Security 2013, so if someone has a different version of the antivirus, then most likely this article will also help him. Now let's begin.
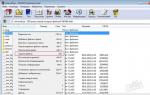
Settings – anti-virus protection – firewall. Click the “Network packet rules” button. We get a list of rules that this moment are working. Some of them prohibit something, others allow it. At the moment everything looks something like this:
If you noticed, the screenshot is not original. I took it from another product - KIS2013, but take my word for it - in KES8 everything was exactly the same. And this is the server where the protection should be on top level! As we can see, there is a lot here and everything is approximately clear: DNS queries (TCP/UDP), sending messages, any activity from trusted networks is completely allowed, from local ones - partially, the port responsible for the remote desktop is disabled, various TCP ports are disabled/ UDP, but activity from outside is partial, at the end of 5 rules of the ICMP protocol. Yes, half the rules are incomprehensible, half are unnecessary. Let's create a sheet from scratch and create our own rules.
The first thing I did was create my favorite rule - Deny All(ban everything)
and placed it down. Then, by searching the Internet, I found out which ports the VPN technology uses. This Protocol 47, which also has the name GRE:
I placed the rule with GRE above the prohibiting rule. Another port that needs to be opened for VPN is 1723 . So I created a rule VPN_IN:
I placed the rule with port 1723 at the very top. I modified the rest of the rules a little, and left some. The result is the following list (Firewall List):
I will comment on each one.
Let me make a reservation right away that you should not completely rely on this article. Perhaps I missed something. I'm not a security guru, so I apologize in advance if I made any mistakes. Criticism, suggestions and praise are welcome, write comments below.
You will also like:
Monitoring server load with Munin
27.02.2015 12:45:58
Antivirus protection is one of the key components of protecting your computer from malware. Antivirus protection must be installed on your computer and updated regularly.
1. Recommendations for setting up Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 for Windows
1.1. Workplace control
1.1.1. Program launch control
This component allows you to track attempts to launch programs by users and regulate the launch of programs using rules. To enable application launch control, you must perform the following steps:
2. In the block Workplace control Choose a section Program launch control;
Enable Application Launch Control;
Save.
1.1.2. Program activity control
This component records the activity performed by programs in the system and regulates the activities of the program depending on their status. To enable application activity control, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Workplace control Choose a section Monitoring program activity;
3. Check the box next to the item Enable Application Privilege Control;
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.1.3. Vulnerability monitoring
This component checks for program vulnerabilities upon startup and then running programs. To enable vulnerability monitoring you must:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Workplace control Choose a section Vulnerability monitoring;
3. Check the box next to the item Enable Vulnerability Monitoring;
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.1.4. Device Control
This component allows you to control the connection of removable devices. To enable device control and select devices, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Workplace control Choose a section Device control;
3. Check the box next to the item Enable Device Control;
4. In the list of devices, select the devices that need to be monitored;
Save.
1.1.5. Web control
This component allows you to control access to web resources depending on their content and location. To enable access control to web resources, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Workplace control Choose a section Web control;
3. Check the box next to the item Enable Web Control;
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.2. Antivirus protection
1.2.1. File antivirus
File Anti-Virus allows you to select one of the preset file security levels or configure them yourself, set the actions that the file anti-virus should perform when an infected file is detected, and select file scanning technologies and modes.
To enable File Anti-Virus, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section File antivirus;
3. Check the box Enable File Anti-Virus.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Security level
- high;
- recommended;
- short.
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section File antivirus;
3. In the block Security level
- Security level
- Settings
In the window that opens File antivirus
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
To change the actions of File Anti-Virus when an infected file is detected, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section File antivirus;
3. In the block, select one of the following parameters:
- Treat
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.2.2. Mail antivirus
Mail antivirus scans incoming and outgoing messages mail messages for the presence of any files that pose a threat to the computer.
To enable Mail Anti-Virus you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section File antivirus;
3. Check the box Enable Mail Anti-Virus;
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Security level
Security levels are different sets of parameters used to protect file system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 for Windows antivirus tool comes pre-installed with three security levels:
- high;
- recommended;
- short.
To change the security level, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Mail antivirus;
3. In the block Security level select one of the following options:
- Security level
Using the slider, select one of 3 preset security levels.
- Settings
In the window that opens Mail antivirus configure the file security level yourself and save your changes.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Actions when threats are detected
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Mail antivirus;
3. In the block Actions to take when a threat is detected select one of the following options:
- Select action automatically
- Perform action: Heal. Remove if treatment is not possible.
- Treat
- Delete if treatment is not possible
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.2.3. Web Antivirus
Web Anti-Virus allows you to protect your computer when working on the Internet.
To enable Web Anti-Virus you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Web Antivirus;
3. Check the box Enable Web Anti-Virus.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Security level
Security levels are different sets of settings used to protect the file system. Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 for Windows antivirus tool comes pre-installed with three security levels:
- high;
- recommended;
- short.
To change the security level of web traffic, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Web Antivirus;
3. In the block Security level select one of the following options:
- Security level
Using the slider, select one of 3 preset security levels.
- Settings
In the window that opens Mail antivirus configure the file security level yourself and save your changes.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Actions when threats are detected
To change the actions of Mail Anti-Virus when an infected message is detected, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Web Antivirus;
3. In the block Actions to take when a threat is detected select one of the following options:
- Select action automatically
- Prohibit downloading.
- Allow downloads
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.2.4. IM Antivirus
IM Anti-Virus allows you to scan traffic transmitted by programs for instant messaging. To enable IM Anti-Virus you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section IM Antivirus;
3. Check the box Enable IM -Antivirus.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Protection area
The protection area refers to objects scanned by IM Anti-Virus during operation. By default, IM Anti-Virus scans incoming and outgoing messages. In order to create a protection area, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section IM Antivirus;
3. In the block Protection area select one of the following:
- Incoming and outgoing messages
When you select this option, IM Anti-Virus will scan all incoming and outgoing messages from instant messaging programs;
- Incoming messages only
When you select this option, IM Anti-Virus will scan only incoming messages from instant messaging programs;
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Verification methods
Setting up the use of heuristic analysis
In order to configure IM Anti-Virus scanning methods, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section IM Antivirus;
3. In the block Verification methods
- Superficial;
- Average;
- Deep.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Configuring IM Anti-Virus to check links against databases of malicious and phishing web addresses
In order to configure IM Anti-Virus checks for links against databases of malicious and phishing web addresses, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section IM Antivirus;
3. In the block Verification methods follow these steps:
- Check links against a database of malicious web addresses
Selecting this option allows you to check links in messages from instant messaging programs to see if they belong to a database of malicious web addresses;
- Check links against a database of phishing web addresses
Selecting this option allows you to check links in messages from instant messaging programs to see if they belong to the database of phishing web addresses.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.2.5. Firewall
Firewall allows you to protect data stored on a computer connected to local network and the Internet. Firewall allows you to detect all network connections on your computer and block all possible threats to the OS.
By default, the firewall is enabled. It is highly not recommended to turn it off. To enable or disable the firewall, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Firewall.
3. Do one of the following:
- Check the box Enable firewall. When you check the box next to this item, Firewall will be enabled.
- Uncheck Enable firewall. If you uncheck the box next to this item, Firewall will be disabled.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.2.6. Defence from network attacks
Protection against network attacks, having detected an attempt to attack a computer, blocks any network activity of the attacking computer in relation to the computer on which the anti-virus protection tool is installed. To enable protection against network attacks, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section Protection against network attacks;
3. Check the box next to the item Enable protection against network attacks;
4. Check the box next to the item Add the attacking computer to the block list on.
Save.
1.2.7. System monitoring
System monitoring collects data about the actions of programs running on the computer. In the future, the collected information can be used in the treatment of programs (rolling back actions performed by malicious programs in the OS), placing the executable file in quarantine if the program’s activity coincides with a pattern of dangerous behavior.
By default, Monitoring is enabled and running. Turning it off is only possible when absolutely necessary and is not recommended.
To turn Monitoring on and off, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section System monitoring;
3. Select one of the following:
- Enable system monitoring.
You must check the box to enable monitoring
- Turn off System Monitoring.
You must clear the checkbox to turn off monitoring.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Setting up system monitoring
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section System monitoring;
3. Check the boxes for the required actions:
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Using patterns of dangerous program behavior
To use templates you must complete the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section System monitoring;
3. In the block Proactive Defense check the box Use updated behavior patterns (BSS).
4. Dropdown When malicious program activity is detected select the required action:
- Select action automatically.
When you select this item, the default actions are performed. By default, the malware executable file is quarantined.
- Move file to quarantine.
When you select this item, the detected malicious file will be moved to quarantine.
- Terminate the malware.
When you select this item, if a malicious program is detected, the antivirus will shut down its work.
- Miss.
When you select this item, if a malicious file is detected, the antivirus does not take any action with it.
Rolling back malware actions during disinfection
To enable or disable the rollback of malware actions during disinfection, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Antivirus protection Choose a section System monitoring;
3. Select one of the following actions:
When you check the box next to this item, when treating malware, the actions performed by these programs in the OS will be rolled back.
If you uncheck the box next to this item, when treating malware, the actions performed by these programs in the OS will not be rolled back.
- Roll back malware actions during disinfection.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.3. Scheduled tasks
Setting up scheduled tasks allows you to carry out any actions within specified time, which ensures that checks and updates are performed regularly.
1.3.1. Update
To set the update execution time, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Update;
3. In the block Startup mode and update source click the button Startup mode...
4. In the window that opens, go to the tab Startup mode. Select one of the following update installation options:
When selecting this item, you must configure Periodicity installing updates.
5. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.3.2. Full check
Security level
To configure the security level for a full scan, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Full check;
3. In the block Security level
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Actions when threats are detected
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Full check;
3. In the block
- Select action automatically
- Perform an action
- Treat
- Remove if treatment is not possible.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Full check;
3. In the block Launch mode and scan objects
- Startup mode
- Manually
- Scheduled.
- Objects to check
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.3.3. Checking Important Areas
To configure the security level for scanning critical areas, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Checking Important Areas;
3. In the block Security level use the slider to select the security level. There are 3 levels:
- Short
- Recommended
- High
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Actions when threats are detected
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Checking Important Areas;
3. In the block Action when a threat is detected you must select one of the following actions:
- Select action automatically
- Perform an action
When you select an item, you can choose the following actions:
- Treat
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Launch mode and scan objects
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Checking Important Areas;
3. In the block Launch mode and scan objects The following parameters need to be configured:
- Startup mode
When you click this button, the settings window will open. You must select one of the launch modes:
- Manually
- Scheduled.
- Objects to check
When you click this button, the settings window will open. It is necessary to mark objects for verification, and you can also add new objects.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
1.3.4. Custom scan
To configure the custom scan security level, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Custom scan;
3. In the block Security level use the slider to select the security level. There are 3 levels:
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Actions when threats are detected
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Custom scan;
3. In the block Action when a threat is detected you must select one of the following actions:
- Select action automatically
- Perform an action
When you select this item, you can choose the following actions:
- Treat
- Remove if treatment is impossible.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
Scan launch mode
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Checking Important Areas;
- In the block Launch mode and scan objects needs to be configured Startup mode
When you click this button, the settings window will open. You must select one of the launch modes:
- Manually
- Scheduled.
Save.
1.3.5. Search for vulnerabilities
Searching for vulnerabilities allows you to regular checks established software on vulnerabilities, thereby allowing you to quickly find out about possible problems and eliminate them in a timely manner.
Objects to check
To configure objects to scan for vulnerabilities, you must perform the following sequence of actions:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Search for vulnerabilities;
3. In the block Objects to check It is necessary to tick the boxes of the manufacturers in whose products it is necessary to search for vulnerabilities:
- Microsoft
- Other manufacturers
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
To configure the vulnerability scan launch mode, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the block Scheduled tasks Choose a section Search for vulnerabilities;
3. In the block Vulnerability scan launch mode You must select one of the following modes for launching a vulnerability scan:
- Manually;
- Scheduled.
- Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button Save.
2. Recommendations for setting up Dr.Web Desktop Security Suite (for Windows workstations), version 6.0
2.1. Notifications
Notifications allow the user to quickly receive information about important events in the work of Dr.Web. To configure notifications, you must complete the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Notifications.
3. Check the box next to the item Use notifications and press the button Notification settings...
4. In the window that appears, select the checkboxes for the notifications you require. When selected, a checkbox can be selected in one of the columns:
- Screen.
When you check the box next to this item, on-screen notifications will be displayed
- Mail.
When you check the box next to this item, notifications will be sent by mail.
5. Set additional options for displaying on-screen notifications:
- Don't show notifications in full screen mode.
Selecting this item allows you not to receive notifications when working with applications in full screen mode.
- Display Firewall notifications on a separate screen in full screen mode.
Selecting this option allows you to display firewall notifications on a separate desktop while applications are running in full screen mode.
6. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.2. Updates
To configure updates, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Update.
3. Select components to be updated:
- All (recommended);
- Bases only.
4. Install Update frequency.
5. Configure the update source by clicking the button Change…
In the window that appears, select one of the update sources:
- Internet (recommended).
When you select this item, updates are installed from the developer’s website.
- Local or network folder.
When you select this item, updates are installed from local or network folder, into which the updates are copied.
- Antivirus network.
When you select this item, updates are installed via a local network from a computer on which the antivirus is installed and an update mirror has been created,
6. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
7. Select a proxy server by clicking the button Change…
In the window that appears, you need to specify the settings for connecting to the proxy server:
- Address
- User
- Password
- Authorization type
8. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
9. Select an update mirror by clicking the button Change…
In the window that appears, specify the path to the folder into which updates will be copied.
10. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
11. Save all changes made by clicking the button OK.
2.3. Antivirus network
Function Antivirus network allows remote control established means antivirus protection from other computers within the same local network on which the same anti-virus protection tools are installed.
To enable this option, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Antivirus network.
3. Check the box next to the item Allow remote control.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.4. Preventive protection
Setting up preventive protection allows you to set how the antivirus protection tool reacts to actions third party applications which can lead to infection of your computer.
Level of preventive protection
To configure the level of preventive protection, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Preventive protection.
3. Set the blocking level for suspicious activities by clicking the button Change….
- Minimum (recommended)
Default level. This level prohibits automatic change system objects, the modification of which clearly indicates an attempt to maliciously influence the OS. Low-level disk access and modification of the HOSTS file are also prohibited.
- Average
This level additionally denies access to those critical objects that could potentially be used by malicious programs.
- Paranoid
If you select this level, you will have access to interactive control over driver loading, automatic start programs and the operation of system services.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
Data Loss Prevention
Data Loss Prevention allows you to create copies of the contents of selected folders, thereby protecting important files from being modified by malware.
To configure data loss prevention, you must complete the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Preventive protection.
3. To configure data loss protection, click the button Change…
4. In the window that opens, select the option Turn off data loss protection
5. To add files that need to be copied, click the button Add
6. Specify the location where copies will be stored and the frequency with which these copies will be created.
7. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
To recover data in case of data loss, follow these steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Preventive protection.
3. Press the button Restore…
4. In the window that opens, select the date for which all specified copies of files will be restored to the specified folder.
5. To start recovery, click the button OK.
2.5. Self-defense
The self-defense function allows you to protect the antivirus protection tool from unauthorized influence.
To enable self-defense you must:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Basic select item Self-defense.
3. Check the box next to the item Enable self-defense.
4. If necessary, check the boxes next to the following items:
- Prohibit emulation of user actions
This option prohibits any changes in the operation of the anti-virus protection tool, except those made manually by the user.
- Prohibit changing the system date and time
This option prohibits manual and automatic changes to system time settings.
- Protect Dr.Web settings with a password
This option allows you to set a password to access the antivirus protection settings.
5. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.6. Email protection
2.7. Excluded Applications
By default, mail traffic of all custom applications on the computer. In order to set an exception - applications whose mail traffic will not be intercepted, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab SpIDer Mail select item Excluded Applications.
3. To add an application to the exception, enter the required name in the input field and click the button Add
4. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.8. Firewall
A firewall helps protect your computer from unauthorized access and prevents important data from leaking over the network. It is highly not recommended to turn it off.
To enable or disable the firewall, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Firewall select item Turn on or Launch.
3. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
To configure the firewall, follow these steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Firewall go to the tab Applications
3. For each application you can:
- Generate a set of filtering rules. To do this you need:
Press the button Create
Change
Copy.
- Delete all rules for the program. To do this you need:
Delete.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.9. Interfaces
In order to set a set of filtering rules for packets transmitted through a specific network interface, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Firewall go to the tab Interfaces
3. Select the required interface from the list and match the required rule from the drop-down list.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.10. Packet filter
To set the packet filter operating parameters, you must perform the following steps:
1. Open the program settings window;
2. In the tab Firewall go to the tab Interfaces and press the button Tune
3. In the firewall settings window, you can do the following:
Generate sets of filtering rules. To do this you need to do the following:
- Create a set of rules for new program. To do this you need:
Press the button Create
- Edit an existing ruleset. To do this you need:
Select an existing ruleset in the list and click the button Change
- Add a copy of an existing ruleset. To do this you need:
Select an existing ruleset and click the button Copy.
- Delete the selected ruleset. To do this you need:
Select the appropriate set of rules and click the button Delete.
4. Save your changes by clicking the button OK.
2.11. Dr.Web scanner
3. Conclusion
Anti-virus protection is undoubtedly one of the important components in ensuring computer security, however, do not forget that anti-virus protection is not a panacea for all threats.
Don't forget about basic settings PC security (""). It is also necessary to remember about Internet security (“”).
Firewall Kaspersky Internet Security, understanding the default settings
Alexander Antipov
The first step to safe travel through the vast expanses of various networks is, of course, installing a reliable means of protection. One of the few such tools is the comprehensive product Kaspersky Internet Security.
The first step to safe travel through the vast expanses of various networks is, of course, installing a reliable means of protection. One of the few such tools is the comprehensive product Kaspersky Internet Security. Despite the fact that the KIS product is quite complex, immediately after installation it is ready to perform all the duties assigned to it. The need for additional settings is extremely rare, and this is a very big plus for developers. But it is necessary to understand that this opportunity is based on the sharp edge of compromise solutions. Let's look at what they are using the example of a firewall.
Firewall settings consist of two parts: program rules and package rules. Using program rules, you can allow or deny certain programs or groups of programs to send or receive packets or establish network connections. Packet rules allow or deny the establishment of incoming or outgoing connections, and the transmission or reception of packets.
Let's see what the rules for programs are.

All programs have four categories:
- Trusted - they are allowed to do everything without exception.
- Weak restrictions - the “action request” rule has been established, allowing the user to independently make a decision about the advisability of network communication between programs of this group.
- Strong restrictions - in terms of permission to work with the network, the same as weak ones.
- Not trusted - by default, these programs are prohibited from any network communication (from a human standpoint, I feel very sorry for them).
By default, all programs from Microsoft, KIS itself and other programs are placed in the “trusted” group famous manufacturers. For the default settings, the choice is good, but personally I would not trust all programs, even from famous manufacturers, so completely.
How do programs fall into one group or another? It's not that simple here. The decision to place a particular program into one of four groups is made based on several criteria:
- Availability of information about the program in KSN ( Kaspersky Security Network).
- The program has a digital signature (already tested).
- Heuristic analysis for unknown programs (something like fortune telling).
- Automatically place a program in a group pre-selected by the user.
All these options are located in the “Application Control” settings. By default, the first three options are installed, the use of which leads to a large number of “trusted” programs. The fourth option can be selected independently as an alternative to the first three.
Let's conduct an experiment. Let’s put some program (for example, the “Opera” browser) in the list of programs with weak restrictions and see how the “action request” rule works. For program rules to take effect, you must close and reopen the program for which the rules have been changed. If you now try to go to any website, no action request will occur, and the program will calmly establish a network connection. As it turns out, the “action request” rule only works if the “Select action automatically” option is unchecked in the main protection settings.
Another surprise awaits users of network utilities such as ping, tracert (if the “action request” rule is extended to trusted programs), putty (ssh client) and, possibly, the like. For them, KIS stubbornly refuses to display the action request screen. There can only be one way out - to set permissions for a specific program manually.
Before moving on to package rules, let me give you one piece of advice: create your own subgroups for each group of programs. For example: “Network utilities”, “Office programs”, “Internet programs”, etc. Firstly, you can always quickly find the desired program, and, secondly, it will be possible to set rules for specific groups, instead of setting rules for individual programs.
Batch rules.

Packet rules define individual characteristics of packets: protocol, direction, local or remote port, network address. Batch rules can act as “allowing”, “denying” and “according to program rules”. The rules are scanned from top to bottom until an allowing or prohibiting rule based on a set of characteristics is found. If a rule for a package is not found, the default rule (the latest one) is applied. Usually in firewalls the last rule is to prohibit the reception and transmission of any packets, but for KIS this rule is permissive.
The action “according to a program rule” is by its nature a “window” for the actual actions of the program rules. This is convenient because you can determine the order in which rules are executed. For example, the program tries to send a packet to port 53 of the DNS server. If there is a packet rule with an action “according to program rules”, direction “outgoing”, remote port 53 (or not defined), and an allowing rule is set for the program to send a packet to port 53, then the packet will be sent if the program is prohibited from sending packets to port 53, then this packet will not be sent.

The scope of the rules covers a certain area: “any address” (all addresses), “subnet address” - here you can select the type of subnet “trusted”, “local” or “public”, and “addresses from the list” - specify IP addresses or domain names manually. The relationship of a specific subnet to “trusted,” “local,” or “public” is set in the general firewall settings.

KIS packet rules, unlike most firewalls, are overloaded with a large number of directions: “inbound”, “inbound (stream)”, “outbound”, “outbound (stream)”, and “inbound/outbound”. Moreover, rules with some combinations of protocol and direction do not work. For example, an ICMP deny rule in combination with stream directions will not work, i.e. prohibited packets will pass through. For some reason, stream directions are applied to UDP packets, although the UDP protocol by its nature does not create a “stream” as such, unlike TCP.
Another, not entirely pleasant, point is that the packet rules do not have the ability to specify a reaction to blocking an incoming packet: prohibit receiving the packet with a notification to the party that sent it, or simply discard the packet. This is the so-called “invisibility” mode, which was previously present in the firewall.
Now let's turn to the rules themselves.
Rules 1 and 2 allow, according to program rules, to send DNS requests via TCP and UDP protocols. Of course, both rules are useful, but basically network programs such as email and browsers request website addresses through the system DNS service, for which the system program"svchost.exe". In turn, the service itself uses very specific DNS server addresses, specified manually or via DHCP. DNS server addresses rarely change, so allowing DNS requests for the “svchost.exe” system service to be sent to fixed domain name servers would be sufficient.
Rule 3 allows programs to send email via TCP. Here, as well as for the first two rules, it would be enough to create a rule for a specific program for working with by email indicating which port and server to send to.
Rule 4 allows any network activity for trusted networks. Be very careful when enabling this rule, do not accidentally confuse the network type. This rule effectively disables firewall functionality on trusted networks.
Rule 5 allows any network activity according to the rules of programs for local networks. Although this rule does not completely disable the firewall, it significantly weakens its control functions. According to the logic of rules 4 and 5, rules would need to be placed at the very top to prevent packets from being processed by rules 1 - 3 when the computer is on a trusted or local network.
Rule 6 prohibits remote control of the computer by RDP protocol. Although the scope of the rule is “all addresses,” it actually only applies to “public networks.”
Rules 7 and 8 prohibit access from the network to network services computer via TCP and UDP protocols. In fact, the rule only applies to “public networks.”
Rules 9 and 10 allow everyone, without exception, to connect to a computer from any network, of course excluding services prohibited by rules 6 - 8. The rule applies only to programs with permitted network activity. But be very careful, network activity is allowed by default to almost all programs except untrusted ones.
Rules 11 - 13 allow the reception of incoming ICMP packets for all programs. These rules make no more sense than 1 - 3, because ICMP in the vast majority of cases is used by the ping and tracert programs.
Rule 14 prohibits the reception of all types of ICMP packets, of course, with the exception of those allowed by rules 11 - 13.
Rule 16 prohibits incoming ICMP v6 echo request. ICMP v6 is not needed in the vast majority of cases. It would be possible to ban it completely.
Rule 17 allows everything that is not expressly permitted or prohibited by the previous rules. Although this rule is not displayed on the screen, it is absolutely necessary to remember its existence.
The default KIS firewall settings are certainly good and are suitable for most home computer users, which is what this product is aimed at. But flexibility and undemanding additional settings, which was mentioned at the beginning of the article, unfortunately is achieved at the expense of the security of the users themselves, making this very security very dependent on the human factor: the knowledge and error-free actions of the user himself.