A wireless modem usually has a range of 30 meters. Many reasons can lower the range and lower the signal. Interference can occur due to the following factors: metal, thick walls, signals from other devices that use wireless frequencies (mobile phones, microwave ovens). Let's sort it out simple ways to strengthen the WiFi signal.
9 Ways to Strengthen a WiFi Router Signal with Your Own Hands
1. Minimize the use of devices at 2.4 GHz frequency
Most often it interferes Appliances: Radio telephones, microwave ovens, security systems, television remote control. You will have to replace the devices or turn them off when using wifi. To check which devices are interfering with our network traffic, you can turn off the devices one by one and look at the signal level. In this case, we will roughly know what is stopping us.
2. Move your router
Sometimes the solution is very simple. You just need to find the highest and most comfortable point for the modem.
- Select a high point on your modem to maximize the effective broadcast range. The higher the better.
- Try placing it in the center of your living space for more area coverage. In the center and high.
- Bring your devices closer to the network if possible.
- Find a place where your neighbor's wifi reception is poor, try placing the modem at that point.
- Move away from any metal: iron shelves, drawers and similar things. (If you use a laptop for example)
- Move away from cordless phones and microwaves.
- Try applying all the above points into one.
3. Change the router broadcast mode
Select the new 802.11 standard N in the modem settings, if supported. 802.11 N offers much greater range and signal strength than 802.11 a/b/g devices. (For the 802.11N broadcast changing function to appear, you need to log in with super admin rights.)

4. Switch the router channel to a free one
Modems operate on channels from 1 to 11. Changing the channel will allow the router to create a clear signal between other wireless devices. For indoor testing, which channel is on? wifi network, you can use the program Acrylic:
- Our network.
- What channel is it on and the 802.11-n broadcast mode.
- Pink is our coverage on channel 10.
- We see that two networks (pink, blue) are on the same channel 1, they interfere with each other.
- You can check the rating status of the setting.
What do we have? Exactly that my neighbors’ two wifi networks are on the same channel, thereby interfering with each other. Choose a channel on which there are fewer wifi networks connected or not connected at all.

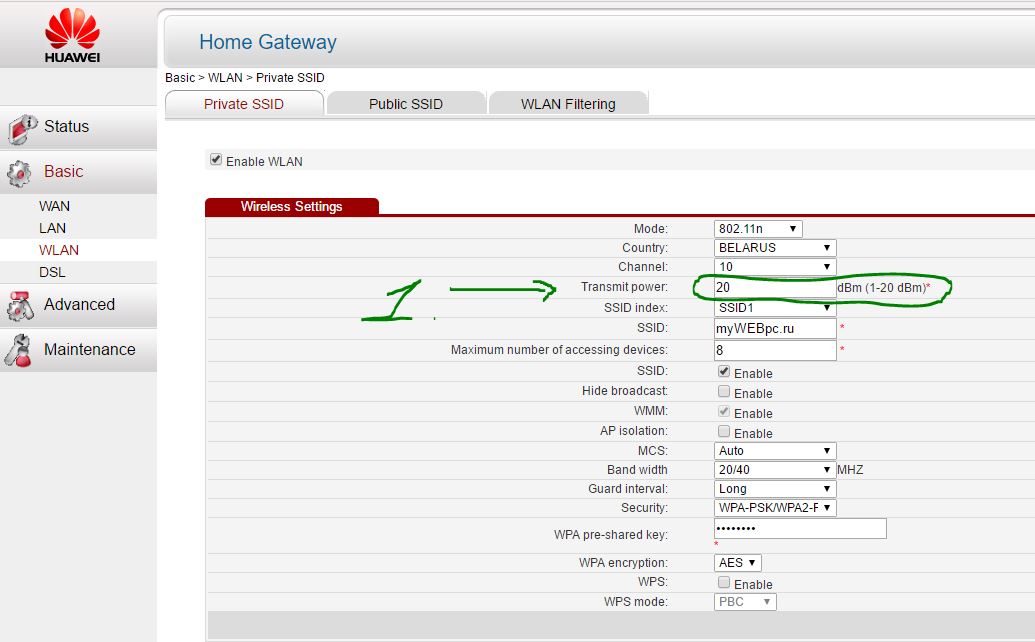
5. Strengthen the router's transmission power
Read the instructions for the probability of the xmit option, the power of your modem: the amount of energy it uses to transmit a signal. You can increase this number to 45 (mW). Be aware that you risk overheating or damaging your router.
An example of two modems. Look for the setting and increase it. In the first picture, select the item High. On the second, enter the maximum value 20 .

6. Change the standard router antenna
Find another antenna from the old router, if it is more powerful, and replace it, which will provide more power. Not all routers allow you to unscrew the antenna as usual. It is attached completely, many do it as in the video.

7. Make a directional wave Wi-Fi
Direct your wifi network not 360 degrees, but less, thereby the remaining waves will be reflected and directed in one direction, which will give a small effect. Cut from beer cans like in the picture. It is best suited when you need to connect two routers operating in the mode: wds, repeater. You must understand that wifi will not work well behind the closed part of the can. This method is how to give a larger target wave coefficient.

8. Install a repeater
Also called "Repeater". Expands the network of the received signal. The repeater receives the signal from the modem and amplifies it to increase the range. Sold as a block that needs to be plugged into an outlet after quick setup. Many routers have a "Repeater" option.

9. Installing a wifi amplifier (Booster)
Connect an amplifier, called a booster, specifically to the modem. A booster is better than a repeater. A repeater only amplifies the strength of the existing signal, and not the strength of the range, which cannot be said about a booster. Use a bi-directional "Booster" to increase speed.

05/23/2016 at 10:59 (4 years ago)
Hello! I feel like Wi-Fi is hitting my body. I want to get my neighbors to reduce power. I and all my neighbors have Ericsson modems with two antennas. Well, a very powerful modem. At night, of course, I turn it off.
05/23/2016 at 11:29 (4 years ago)
Hello. If you're interested in my opinion, I very much doubt that Wi-Fi can harm the body. Yes, it definitely won’t improve your health, but it’s unlikely to directly feel the effect of Wi-Fi on the body.
So are two antennas. They do not mean that the modems are emitting a strong signal. And the Wi-Fi signal itself cannot be very strong. It is limited there, in accordance with the law, as far as I know.
An ordinary mobile phone has a much stronger effect on the body compared to Wi-Fi. It is a fact.
Personally, I am of this opinion: it is best to install the router in the room where you are least likely to be. For example, in the corridor. And where do you not sleep? And turn it off at night if you wish. You can set it to turn off automatically. But not all routers have this.
05/03/2017 at 20:58 (3 years ago)
No one listens to the radio at full volume when they are next to it because the long evolution of man gave him an organ (ear) with a pain threshold for loud sound! But it did not give a person an organ that signals an excess of microwave energy, because There were no such sources in abundance near humans! But such an “organ” can easily “appear” in the form of something, for example, like hair loss or cellular pathology with pain if we ourselves do not take care of the sanitary environment around us. So it is imperative to reduce the power to the necessary and sufficient level, comrades! And it’s even better not to chase Wi-Fi freebies (as you know: Free cheese...), and use wired technologies or telephone Internet, which emits only when exchanging information with the base station (as Alternative option, where possible).
08/10/2017 at 09:45 (3 years ago)
In an apartment building, the number of devices operating in the 2.4 GHz band (hazardous for biological objects) is commensurate with the number of residents. The intensity of the total field in some areas may exceed the limits allowed by Sanpin. And then draw your own conclusion whether it’s worth the risk or not.
05/05/2017 at 20:47 (3 years ago)
I completely agree! Everyone would do this! I also feel the harm. The problem with Wi-Fi is that its emitter is in close proximity to a person, and all comparisons with the radio waves that we are surrounded by are completely incorrect (both with phones and microwaves, since they emit for a short time, and not around the clock like Wi-Fi !) After all, the signal from radio waves on receivers rarely even reaches 100% according to the reception indicator because their sources are very far away! And the harmfulness increases sharply when approaching the transmitter at a “critical” distance. For example, if when approaching a radio wave source at a distance of 8 meters, the signal level has reached 100%, then what the radiation level will be at a closer distance can only be calculated, because Gadgets don’t show us the “off-scale” level. Further, reducing the distance to 2m. (i.e. 4 times, here is a quadratic dependence) we get 400% of the signal (up to 1 m - the distance is 8 times, and the level is 8 * 8 = 64 times, i.e. 6400% (!) of the nominal, etc. .. Avoid such redundancy!) . Everyone talks about power, about harmfulness, but they don’t say at what DISTANCE they measure it! Because theoretically, as the distance tends to zero, the impact begins to tend to infinity! Therefore, reduce the power to levels of 10-80% in your apartments, and do not be lazy to turn it off at night when you are not using it, or leave the house, because the harm from your neighbors’ routers is also applied to your body (Alexander counted 65 points!!!). Cellular telephone safer because one emitter is very far away ( base station), and the emitter in the device, although close, emits only during a conversation, which is why they say that they should not talk for a long time for safety.
09.18.2019 at 01:23 (5 months ago)
Solidarity. Because If you think logically, then you will come to this. (And, in principle, I had the same opinion before reading it). But why the author (Sergey) writes (in the com.) that the telephone is more dangerous is not clear. Do they write on the Internet? they write a lot. But they don’t explain, and apparently they copy from each other, not understanding what they are writing about. I heard a ringing, but don’t know where it is.
What kind of radiation does a phone create in passive mode? (i.e. receiver). There’s no escape from the network signal anyway—you’ll have to run far))). We are not talking about such insignificant signals. Further. How much energy does the phone consume in receiver mode (its tiny battery lasts on average for a week - it doesn’t matter if it’s a little less). Here I looked at the battery 2.41 Wh (that is, the capacity (total). Divide by 7 days (or 168 hours) = 0.014 W (approximately) i.e. per hour. - Provided that the battery is new, which is a rather rare phenomenon)). Well, in talk mode the phone will work for 1 -1.5 hours. That is. consumption - well, let it be 2 watts. And this figure is only approaching the power of the router.
And now, how much does the router (Wi-Fi)) router) consume in normal mode (operation). Now I’ll look. 4 watts (at 100%), and 3 watts (15%). (And I have such a small TOTOLIHK) And if They don’t lie in the percentage settings, then according to some calculations it can be assumed that the signal takes a little more than 1 Watt (at 100%) I don’t think that the loss is about 3 Watts. And practice shows that the signal (i.e. Wi-Fi level) changes slightly - between 100 and 15%. Therefore, based on some considerations (mainly taking into account heating), we can assume that the cost of the signal will most likely be about 3 watts (2, 5). And common sense suggests that this figure will be closer to the latter - we don’t live in the Middle Ages))). (At most, 2 watts).
So we have two numbers 0.014 W/h (tel-n) and 2.5 W/h (router). All this is approximately of course, and the numbers may differ several times (for both indicators). Nevertheless, the difference was 178 times (Guess who won)). In fact, it is even greater, because in a phone (0.014 Wh) this is only the power consumed, and the signal power will, of course, be less. And only when talking do these numbers come closer to each other (about 2-2.5 watts).
Of course, a lot is not taken into account here (including we do not know what exactly these waves are (in each case) and how they affect health). But I think no one will deny the dependence of signal strength on power consumption.
Now let's take one more fact. Probably everyone has heard about how phones affect us when we are eating in a minibus, when someone is talking (AFTER THE SAME WE WRITTEN ABOUT THIS).
DOESN'T IT SEEK IT STRANGE TO YOU THAT A PHONE IS HARMFUL, BUT A ROUTER WHICH MATCHES THE PHONE (TRANSFER) IN POWER IS NOT., AND WHO BENEFITES. AND WHY THERE ARE SO MANY NOW, ALMOST EVERYONE WITH A ROUTER, AND THEY GROW AROUND US LIKE MUSHROOMS. AND WE ARE NOT TALKING ABOUT 5G. I HOPE YOU WILL GUESS IT.
WHY DO I HAVE A ROUTER??? — GAVE IT FOR FREE BECAUSE I DO NOT INTEND TO USE IT IN WI-FI MODE. (MOSTLY). SENSE PEOPLE WRITE THAT IN THE FUTURE PEOPLE SHOULD LAY CABLES IN THE WALL. (ALTHOUGH NOTHING IS PRESENTING THEM FROM LAYING THEM NOW ALONG THE SKIRTINTH) BECAUSE THE ROUTER (ROUTER HAS 4 JACKS (FOR LAN). ACCORDINGLY MOVE THE LAPTOP WHERE YOUR SOUL WISHES (IF THERE IS A CABLE). YES AT LEAST IN ONE PLACE.- AND IF NEEDS - INCLUDE WI-FI. EVEN EVEN IN THE SETTINGS. AND WHAT YOU WANTED - HEALTH IS MORE EXPENSIVE. ALSO AN OPTION: THE LAPTOP NEAR THE ROUTER, TURN ON THE ROUTER, TURN ON THE LAPTOP. (EVERYTHING BY CABLE, WI-FI IS TURNED OFF), YOU NEED TO WALK AWAY - TURN ON WI-FI. A TO THE NEIGHBORS -TUMAKOV)))
AND WHAT ABOUT THE HARM OF WI-FI. STILL, THOUGH IT’S NOT SO LOUD, BUT THEY ALSO WRITE ABOUT THE DAMAGE TO CHILDREN. (BECAUSE THE SKULL BONES) ARE THINNIER.. BUT IS THAT WHY IT’S HARMFUL FOR ADULTS?? After all, WHOEVER READS BETWEEN THE LINES HAS ALREADY READ IT A LONG TIME LONG ago (as long as he can be).
YES, THAT'S WHEN SOMEONE'S TALKING ON THE PHONE. CLOSE (ON THE MINUTES) IS HARMFUL, BUT PUTTING IT TO YOUR EAR FOR UP TO 20 -30 MINUTES A DAY IS NO.- PARADOX.- RIGHT??))))

For many who are just starting their acquaintance with WiFi, technical specifications wireless equipment may seem unclear. Especially if the specification is on English language, as in the case of MikroTik, Ubiquiti and other vendors.
Let's try to look at some of the most important parameters - what they mean, what they affect, in what cases and what you need to pay attention to.
Transmitter Power (Tx Power, Output Power)
Various units measurements. Some manufacturers indicate power inmW, some - in dBm. Translate dBm to mW and vice versa, without bothering yourself with recalculation formulas, possible using .
It is worth noting that the relationship between these two power representations is non-linear. This is easy to see when comparing the ready-made values in the correspondence table, which is located on the same page as the above calculator:
- Power increase at 3 dBm gives an increase in mW 2 times.
- Power increase on 10 dBm gives an increase in mW 10 times.
- Power increase by 20 dBm gives an increase in mW 100 times.
That is, by decreasing or increasing the power in the settings by “only” 3 dBm, we actually decrease or increase it by 2 times.
The bigger, the better? Theoretically, there is a direct relationship - the more power, the better, The further the signal “beats”, the greater the throughput (the amount of data transmitted). For point-to-point backbones with directional antennas raised in open spaces, this works. However, in many other cases, things are not so straightforward.
- Interference in the city. Cranking up the power to maximum can do more harm than good in urban environments. Too strong a signal, reflected from numerous obstacles, creates a lot of interference, and ultimately negates all the benefits of high power.
- Air pollution. An unreasonably strong signal “clogs” the transmission channel and creates interference for other participants in the WiFi traffic.
- Synchronization with low-power devices. It may be necessary to reduce TX Power When connecting to low power devices. For good connection quality, especially two-way traffic, such as interactive applications, online games, etc., you need to achieve symmetry in speed for incoming and outgoing data. If the difference in signal strength between the transmitting and receiving devices is significant, this will not have the best effect on the connection.
There should be exactly as much power as needed. Even if it is recommended to first reduce the power to a minimum and gradually increase it until best quality signal. Wherein remember the nonlinear relationship between the power expressed in dBm and the actual energy power, as we discussed at the beginning of the article.
It is also important to consider that range and speed depend not only on power, but also on the antenna gain (gain), receiver sensitivity, etc.
Receiver sensitivity (Sensitivity, Rx Power)
WiFi receiver sensitivity is the minimum level of incoming signal that the device can receive. This value determines how weak signals the receiver can decipher (demodulate).
Accordingly, you can select equipment for the conditions in which you want to increase your wireless connection.
“Weak” in this case does not necessarily mean “not powerful enough.”A weak signal can be as a result of natural attenuation during long-distance transmission (the farther from the source, the more weaker level signal), absorption by obstacles, and as a result of a poor (low) signal-to-noise ratio. The latter is important because high level noise drowns out and distorts the main signal, to the point that the receiving device cannot “select” it from the general stream and decipher it.
Sensitivity (RX Power) is the second important factor affecting communication range and transmission speed. The greater the absolute value of the sensitivity, the better (for example, a sensitivity of -60 dBm is worse than -90 dBm).
Why is sensitivity displayed with a minus sign?Sensitivity is determined similarly to power in dBm, but with a minus sign. The reason for this is the definition of dBm as a unit of measurement. This is a relative value and the starting point is 1 mW. 0 dBm = 1 mW. Moreover, the ratios and scale of these quantities are arranged in a peculiar way: with an increase in power in mW several times, dBm power increases for several units(same as power).
- The power of radio transmitters is greater than 1 mW, therefore it is expressed in positive values.
- The sensitivity of radio transmitters, or more precisely, the level of the incoming signal, is always much less than 1 mW, so it is customary to express it in negative values.
It is simply inconvenient to present sensitivity in mW, since it will contain numbers such as 0.00000005 mW, for example. And when expressing sensitivity in dBm, we see more understandable -73 dBm, -60dBm.

Sensitivity is an ambiguous parameter in the characteristics of access points, routers, etc. (however, like power, in fact). In reality, it depends on the signal transmission speed and in the equipment characteristics it is usually indicated not by one number, but by an entire table:

The screenshot from the specification lists the various transfer options WiFi signal(MCS0, MCS1, etc.) and what signal power and sensitivity the device with them shows.
Here we run into another question - what do all these abbreviations mean ( MCS0, MCS1, 64-QAM, etc.) in the specifications, and how can we still use them to determine the sensitivity of a point?
What is MCS (Modulation and Coding Scheme)?
MCS in English stands for "modulation and coding schemes". In everyday life it is sometimes called simply “modulation”, although in relation to MCS this is not entirely true.
To coordinate spatial flows between different devices and increase transmission efficiency, signal modulation has been used in radio engineering for quite some time. Modulation is when a signal with information is superimposed on the carrier frequency, modified in a certain way (encryption, changing amplitude, phase, etc.).
The result is a modulated signal. Over time, more and more new ones are invented effective methods modulation.
But the MCS index, which is established by IEEE standards, means not just signal modulation, but a set of parameters for its transmission:
- modulation type,
- information encoding speed,
- number of spatial streams (antennas) used during transmission,
- transmission channel width,
- duration of the protective interval.
The result is a certain channel speed obtained when transmitting a signal, taking into account each of these sets.
For example, if we choose from the above specification the best combination of power (26 dBm) and sensitivity (-96 dBm) is MCS0.
Let's look at the correspondence table and see what kind of transmission parameters MCS0 has. Frankly speaking, sad parameters:
- 1 antenna (1 spatial stream)
- Transfer speeds from 6.5 Mbit/s on a 20 MHz channel to 15 Mbit/s on a 40 MHz channel.
That is, the point provides the above signal power and sensitivity only at such low speeds.
When determining sensitivity (and power), it is better for us to focus on the MCS indices in the specification (datasheet) with more efficient, standard transmission parameters.
For example, in the same specification for Nanobeam, let’s take MCS15: power 23 dBm, sensitivity -75 dBm. In the table, this index corresponds to 2 spatial streams (2 antennas) and a speed from 130 Mbit/s on a 20 MHz channel to 300 Mbit/s on 40 MHz.
Actually, it is precisely these parameters (2 antennas, 20 MHz, 130/144.4 Mbit/s) that Nanobeam works in most cases (MCS15 in the Max Tx Rate field in AirOS is usually set by default).
Thus, the standard, that is, most often used, sensitivity is: -75 dBm.
However, it should be taken into account that sometimes it is more necessary not to high speed, and link stability, or range, in these cases in the settings you can change the modulation to MCS0 and other low channel rates.
The MCS index table (or speed table, as it is sometimes called) is also used for reverse search: they calculate what speed can be achieved at a certain power and sensitivity.
Bandwidth (Channel Sizes)
WiFi uses the division of the entire frequency into channels to transmit data. This allows you to streamline the distribution of radio frequency air between different devices- each equipment can choose a less noisy channel for operation.
In simple terms, this division can be compared to a highway. Imagine what would happen if the entire road was one continuous strip (even one-way) with a stream of cars. But 3-4 lanes already bring a certain order to traffic.
Add and divide. The standard channel width in WiFi is 20 MHz. Starting with 802.11n, the possibility of combining channels was proposed and regulated. We take 2 channels at 20 MHz and get 1 at 40 MHz. For what? To increase speed and throughput. Wider bandwidth means more data can be transmitted.

Disadvantage of wide channels: more interference and shorter data transmission distance.
There is also a reverse modification of channels by manufacturers: reducing their width: 5, 10 MHz. Narrow channels provide greater transmission range, but lower speed.
The modified channel width (reduced or increased) is The width of the line.
What does it affect: on throughput and the “range” of the signal, the presence of several bands - for the possibility of fine-tuning these characteristics.
Antenna Gain (Gain)
This is another important parameter that affects signal range and throughput.
website
Basic parameters for choosing a Wi-Fi router
Long gone are the days when the whole family had, at best, one computer at home. In the modern world we are surrounded by the most various devices, with which you can access the Internet. To organize shared access to the World Wide Web of all this equipment, you can use one of your home computers - however, you will have access to the Network as long as it is turned on. You can also install a server, but this requires certain knowledge to configure it, and the price is not always justified. Fortunately, there is another device that can solve this problem - a router, sometimes called a router.
So, the two main functions of a router are combining various equipment into a local network and providing general access to the Internet channel. Routers are sometimes confused with switches and endpoints. Wi-Fi access, this is due to the fact that they perform fairly similar tasks. But, unlike routers, these devices only allow you to create a local network, a switch - wired, and an access point - wireless.
Routers also come in both wired and wireless, the price difference between them is small, and the functions they perform are almost the same. We will talk about wireless models, although much of what has been said also applies to wired analogues.

Scheme of organizing a network using a router
A fairly large number of manufacturers are involved in the production of routers, but still there are not so many main players, you have probably already heard about most of them. ASUS is one of the world's largest suppliers of not only network equipment, but also various computer components and finished products; routers under this brand are reliable and well-equipped. D-Link at one time became popular thanks to inexpensive models of ADSL modems, in currently it is one of the leaders in the production of routers, modems and network cards. But the TP-LINK company offers router models that have good equipment at a low price. Zyxel is one of the veterans in the production of components for building a network; the products of this company have always been distinguished by their reliability and quality. Linksys- trademark Cisco, one of the leaders in the production of industrial networking equipment, whose advanced achievements are embodied in these models. offers various devices that are distinguished primarily by their unusual design, thanks to which these models can become a noticeable part of the interior. At the same time, the equipment of these models remains at the proper level.

Some Belkin models: N750 DB, Double N+, N1 Vision
A router, as a rule, has one port for external connections, called a WAN port, and several for connecting computers within the network - LAN ports. Wireless models may have one or more antennas, but in some cases they are hidden inside the case. Routers are quite compact in size. For example, the common D-Link DIR-300/NRU has dimensions of 14.7x11.32x3.15 cm - quite small for stationary use; if you often need to use a router when traveling and on business trips, you should take a closer look at compact devices, for example ASUS WL-530g, which measures only 12.9 x 4.4 x 2.9 cm.

Compact ASUS model WL-530g
Main characteristics
Let's figure out what you need to pay attention to first when choosing a router, and start with the key characteristics. One of the important parameters is the type of WAN port used in the device - the most common today are ADSL and Ethernet. If you are not sure which one to choose, check with your Internet provider. In addition, there are routers that use the channel mobile Internet as an external connection or having a USB port for connecting a 3G modem, such as the D-Link DIR-412 model.
The second important characteristic is the supported external connection protocols. The most common ones are "static IP", "dynamic IP", PPPoE, L2TP and PPTP. We won’t go into the details of each technology: you just need to check which one is used by your provider and choose a device that supports it. Fortunately, most famous manufacturers routers provided good support for these protocols and adapted them to the specific application in Russia. Also some providers use MAC address binding network card to the computer's IP address. In such cases, you won’t be able to simply connect a router instead of a computer and set it up right away - you need to contact the service technical support provider. But you can do it easier and use the function of copying the MAC address from the computer to the router, which is found in almost all modern models.
The third important characteristic when choosing a router is the number of ports and the speed of wired and wireless data transfer channels inside local network. All modern routers, except for some compact models, usually have 4 Ethernet ports for wired connections (LAN ports) supporting speeds of 100 Mbit/s or 1 Gbit/s. Today, the most common are hundred-megabit networks; in most cases, their speed is sufficient for data transmission. But gigabit hardware is becoming increasingly popular, and its use will soon become standard in computing. Therefore, you should give preference to models that support a gigabit connection, and buying a hundred-megabit device only if necessary will save a little on the cost.
If you are building a wireless network at home, there are some things to consider important nuances. So, in real conditions, the connection speed will always be lower than that stated in the standard and on the box with the device. This is due to the fact that part of the channel is used to encrypt the transmitted data, as well as maintain the quality of the connection, which very much depends on the barriers between the network equipment. Walls, other Wi-Fi networks or, for example, a microwave oven operating nearby can create significant interference, forcing you to use part of the channel to restore information, thereby reducing the useful flow. In addition, the entire wireless network will operate at the speed of the slowest element connected to it. This leads to the fact that if at least one 802.11g device is connected to the 802.11n network, the transfer speed will be no more than 54 Mbit/s.
For building home network You should choose a router that supports the 802.11n standard with speeds up to 300 Mbps. You should be especially careful when choosing equipment if you are going to transmit video over a Wi-Fi network. In this case, it is worth, among other things, choosing a model with support for two frequency ranges- 2.4 and 5 GHz. Due to the fact that the second band is used much less frequently than the first and has more free channels for transmission, the speed can be higher and, most importantly, more stable. It is only important that other devices on the network support this mode. In addition, some models can create two networks simultaneously, one of which can be used to transmit speed-demanding traffic, and the second to connect all other equipment. Buying a model that supports 450 Mbit/s speed will be more of a foundation for the future, since there are still few devices supporting this speed today. Unfortunately, high-speed routers are more expensive, sometimes significantly more, than their slower counterparts. Therefore, in some cases it may be wise to look at 802.11n devices that support 150 Mbps speeds.
Additional features
In addition to their main purpose, some routers can perform a number of useful functions. Support for the print server option allows you to connect a printer to the router using a USB port and provide access to it from any computer on the network. Some models support connecting an external USB storage device, for example hard drive or flash drives. This opens the ability to access files on the disk, such as music or movies, from any device on the network - these are network-attached storage (NAS) functions. And some routers support working as a torrent client, so you can download various files from the Internet using this popular protocol without using a computer.
If you need to organize Wi-Fi coverage over a fairly large area, for example in an educational building, you should take a closer look at models that support the technology wireless system WDS distributions. It allows you to combine several routers and access points into a common wireless network, thereby expanding the overall coverage area. Sometimes routers have to be installed in places without access to a power outlet. One solution to this problem may be to select a device that supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology; in this case, the router is powered directly via an Ethernet cable, as in the TP-Link TL-WR743 ND model.
Security wireless network
If it is not so easy to intercept information on wired networks, then you can connect to an unsecured wireless network from any laptop, located several tens of meters away. To prevent data interception, various Wi-Fi traffic encryption standards are used, the most common of which are WEP, WPA and WPA2, which are supported by most wireless devices. The first of them does not provide a sufficient level of protection and can be easily hacked by attackers, so it is better not to use it. For protection, you should choose the more reliable WPA or WPA2 protocols; these encryption methods provide a high level of protection, making it almost impossible to hack the network and intercept data.
Also among additional features Every modern router contains tools that allow you to configure security when computers operate on the network. Most often, this is a firewall, which is necessary to control the passing traffic, as well as a DMZ - a “demilitarized zone”, which allows you to configure restrictions on access to local network resources from the outside. In addition, in routers you can find the function " parental controls", with which you can set rules for user access to the Internet at different times and days of the week, as well as limit the ability to visit certain sites.
Radiation
When using modern technology, including Wi-Fi equipment, many of us are concerned about electromagnetic radiation and its impact on health. It should be noted that the radiation power of home routers is limited to 100 mW, which is up to ten times less than mobile phones, - today this level is considered completely safe for the human body. But many models allow you to reduce even this power in the settings. In addition, you should choose a device with a shutdown button wireless module or the entire router when not in use.
Of course, there are subtleties when choosing a router for home use more than enough and it will not be possible to describe them all within the framework of this article. When choosing a device, focus primarily on the functions you expect from the router. If you just need general access to the Internet, choose inexpensive model with a minimum set of functions. If you need a device to perform specific tasks, pay attention to the availability of certain options.
In this review we will try to answer the question: is it enough to install a powerful WiFi router to increase the range? wireless communication? The problem is this. Communication between a computer and a router involves two-way data transfer. That is, a radio transmitter installed in the Wi-Fi card of the computer will be used. But the power of the latter, in most cases, cannot be increased above a certain threshold.
The point here, oddly enough, is not a matter of physics. For certain purposes (maybe to protect health or something else), an interesting law was passed. According to it, the value of the transmitter power for subscriber Wi-Fi devices is clearly limited. The transmitter power cannot exceed 20 dBm.
Home Wi-Fi network
Let's consider small example. The TL-WN7200ND is Wi-Fi adapter for computer. The power of its transmitter, according to some sources, is 26 dBm (0.4 Watt). Well, such a value means four times more power than 20 dBm (0.1 Watt). Therefore, the Windows driver for this adapter contains a corresponding “correction”. Which cannot be turned off.
Thus, if you install the most powerful WiFi router that you can buy now, this will not have a positive effect on the communication range. The problem will remain in subscriber devices. Theoretically, it is possible to “unblock” the driver. Just remember that such actions will be a direct violation of the law (and, in particular, sanitary standards). Which is unlikely to please all users without exception.
Additionally, we note that for routers there is also a similar limitation. The transmitter power of the base device should not exceed 24 dBm (0.25 Watt).
There are two methods to increase the communication range “legally”: connect a highly directional Wi-Fi antenna, or install another router (repeater).
Increasing communication range is “legal”
Can a passive antenna boost the signal?
If you do not take into account losses in the wire, then the gain of an “omnidirectional” antenna is exactly zero decibels. Now imagine that the radiation pattern has been “narrowed” to a half-space. There was all the space, but only half remained - and the intensity doubled. At the same transmitter power.
There are antennas with a very narrow “coverage” of space and with high gain. If doubling the intensity is indicated by the inscription “+3 dB”, then multiplying by four times is “+6 dB”, etc. In most cases, a powerful router is not needed. The question is where exactly in the apartment you need to get Wi-Fi.
If it's enough to Wi-Fi network was accessible inside one room, then an antenna with a 90-degree diagram is fixed in the corner. Nothing more is required. As a result, the intensity will increase four times (when compared with a conventional whip antenna).

Antenna with 90 degree radiation pattern
Of course, to do this, the router’s antenna must be removable (usually an SMA connector is used). The problem of low transmitter power in subscriber devices is also solved in the same way. However, this is only good for desktop PCs.
The most powerful Wi-Fi router, which is mass-produced, has a transmitter power of 0.6 Watt. In Russia, as we have already said, a maximum of 0.25 Watt is allowed, but the intensity can be increased significantly with the help of a “cunning” antenna.
Wi-Fi repeaters
Principle of operation Wi-Fi repeater, or repeater, is clear from the following diagram:

Repeater operating principle
Actually, a repeater is a device that, like a router, will have to be configured. There can be several wireless networks at one point in space, and the device will “relay” one of them (the one needed by the user).
Most office routers equipped with a Wi-Fi module can be used as a repeater. The power of the WiFi router used as a repeater is a very important parameter. But compatibility is even more important (that is, the repeater must support the required Wi-Fi communication protocol). Let's look at an example setup.
When setting the wireless network parameters, you need to select the operating mode: Universal Repeater. Other settings such as band width (20 MHz or 40), baud rate, etc. – must completely match the parameters of the “relayed” Wi-Fi network:

Setting up the router in repeater mode

List of available wireless networks
Here you need to select one required network, click “Connect” and follow the instructions of the setup wizard. If the wireless network uses encryption, then the password and protocol for it are set on the “Wireless Security” tab. As it were, that’s all. Happy setup!
Methods for increasing transmitter power
Accepted notation system
In general, as you know, the unit of power is one Watt, and power should be denoted by Watts. In radio engineering, it is customary to use another scale, in the so-called “Decibels per milliwatt”, dBm.
Zero dBm is 1 milliwatt. Three dBm – 2 mW. And so on. You can remember the reference values: 20 dBm is equal to 100 mW (or 0.1 W), and 23 dBm is 0.2 Watt.
The manufacturer lists the transmitter power in “dBm” (which can easily be converted to Watts if required).
Increasing the power of Wi-Fi transmitters
First, you need to find out how to increase the power of the router “software”. The settings usually do not specify its maximum value.

Setting the transmitter power in D-Link routers
- You need to set the maximum power value in the router
- Then, you need to try to “programmatically” increase the power in subscriber devices
- If these measures are not enough, instead of an external passive antenna, connect a Wi-Fi amplifier with an external antenna (or an active antenna)
An amplifier or active antenna can be connected to both the router and subscriber devices. This “rig” looks something like this:

Wi-Fi amplifier + regular whip antenna
The output power of amplifiers is usually units of watts (2 W or 4 W). As we have already said, the use of such solutions violates the requirements of the law.
Additionally, we note the following. The use of transmitters with a power of more than 20 dBm (or more than 24 dBm for a basic device) is contrary to sanitary requirements. That is, it is harmful to health.