When Mikrotik introduced hAP lite at one time, this became a real impetus for the wider use of routers from this company. An excellent set of features, rich functionality, flexibility, reliability and affordable price have turned it into a real bestseller, which to this day tops the sales ratings of many online stores.
Meet hAP ac²!
Many people mistakenly consider hAP ac² to be a replacement for the previous flagship hAP, this is partly true, but not entirely. We'll figure out.
hAP ac² is supplied in the usual cardboard packaging, the only thing that has changed over the past few years is the pattern added to the box and reminiscent of an embroidered shirt.
As before, the device is supplied without a patch cord and color printing. However, many would probably not refuse a high-quality patch cord.


Due to the matte soft-touch coating, hAP ac² is packaged in polyethylene, which should ensure safety until the device reaches the end customer.
Of the non-standard options, the package includes only a mounting bracket and a short illustrated instruction manual for using this very stand.
The model's article number turned out to be quite intricate - RBD52G-5HacD2HnD-TC, while for the same hEX users could sometimes use an article identifier when communicating on forums, in the case of this model, not everyone will be able to remember the article the first time.

However, you can glean a lot of information from the article:
RB - RouterBOARD
D - Dual-Chain (Full)
52 - Dual-Band 5 + 2.4 GHz
G - Gigabit Ethernet
5HacD - 5 GHz 802.11ac, High-Power (type 1), Dual-Chain
2HnD - 2.4 GHz 802.11n, High-Power (type 1), Dual-Chain
As for the transmitter power, Mikrotik has 4 gradations:
normal power (no index), less than 23-24 dBm;
H - increased power, 23-27 dBm;
HP - high power, 25-29 dBm;
SHP - very high power, more than 27-30 dBm;
Actually, “type 1” means the index “H”. But the index “U” (USB) is not used in the name, although this interface is present here.
In general, the design itself is quite unusual. The company continues to experiment with Tower-Case; at one time, the first “experimental” device was the hAP lite TC. Then hAP ac lite TC (RB952Ui-5ac2nD-TC) and hAP mini (RB931-2nD) appeared.
Surveys show that almost 70% of respondents approve of the domesticated design of hAP ac2.

The indicators and the interfaces themselves are located on opposite sides, which is a standard for home and SOHO solutions. The port indication is not very convenient, but it is not intrusive and will not bother you with its operation at night.
All 5 interfaces are shielded, and there is no possibility of grounding connection on the case.

In addition to the power indicator, hAP ac² also has an additional custom indicator, which is convenient to configure, for example, for the VPN connection status.
The WPS and reset buttons are combined, there is no longer a need to carry a paperclip with you, now a pen or pencil will do - holding the button for a long time is still inconvenient, which will protect against accidental reset.
One of the highlights of the hAP ac² design is the stand.



This is not just a stand, it is a fastening element for installation on a ceiling or wall. We have already installed one of our clients this device specifically on a plasterboard ceiling. The installation process is quick and convenient; with a placement height of 4 meters, there are absolutely no problems with the quality of the coating.
The element is attached with a latch to the bottom edge or cover. In the first case, you will receive a tabletop standing version, in the second - a tabletop lying version, or a wall (ceiling) mount. The legs have silicone inserts that provide anti-slip properties to the stand.
The ac2 itself is extremely compact; the size of the new product is comparable to a regular hAP lite, and in a standing position it takes up minimal space.
Filling Mikrotik hAP ac²
Many owners tried to look into the insides of ac^2, but not everyone succumbed to it; some of those who succumbed to it simply broke the latches. For this reason, we urge you to refrain from opening this model.
The first thing you should pay attention to is the closedness of the internal space of the case. That is, there are ventilation “slots” on the front panel, but it cannot be said that they particularly improve ventilation. The filling of the device easily warms up to 45 degrees when idle, and during load it can rise to 52 degrees.

There is no need to panic about this; the previous hAP ac was much hotter. The device that we chose as a server even warms up to 62-65 degrees when idle.
Almost half of the upper part of the RBD52G-5HacD2HnD-TC board is covered with a massive needle-type heatsink.

On the same side of the board there are 2 antennas, interfaces, a power subsystem and a USB port.

There are 4 mounting holes along the perimeter of the board; the company has probably previously experimented with different housing options, including the classic one.
All the main contents of hAP ac^2 are located on the back side of the PCB.


The device is based on the IPQ-4018 chip manufactured by Qualcomm. This is a highly integrated solution combining a 32-bit ARM processor and wireless modules.


Despite the great similarity with IPQ-4019, these 2 chips are not interchangeable. The older IPQ-4019 has a larger physical size, a different design and wiring diagram.

Although in general, IPQ-4018 and IPQ-4019 differ only in the set of interfaces.
Main computing unit IPQ-4018 is powered by 4 ARM Cortex A7 cores with a clock frequency of 717 MHz. The chip includes a Hardware NAT and Crypto Engine block. As you might guess, the first block is responsible for NAT offloading, the second for hardware encryption.
Both wireless modules have a MIMO 2x2 (Dual-Chain) configuration, and each module has its own co-processor that provides hardware offloading. In the block diagram they are designated as CPU#1 and CPU#2.
At the output of each chain, one amplification unit is wired (hidden under the screens), for a total of 4 of them.

If you look at the official hAP ac2 block diagram, it lists the AR8327 gigabit switch and labels it as being built directly into the IPQ-4018.
At the same time, a QCA8075 is soldered on the board next to the processor, which implements 5 gigabit ports.
If we return to the official block diagram of Qualcomm, the “5GE L2/3/4 Switch Engine” is indicated as part of the IPQ-4018, and the external unit “QFE8075/2 (5/2 ports PHY)” is indicated a little to the left of the diagram.
Thus, in fact, physical layer(PHY) is implemented on a separate external QCA8075 chip, but the remaining wiring is located directly in the SoC. RouterOS itself identifies the switch as an Atheros-8327.
As usual, there is not a lot of permanent memory - only 16 MB (Winbond 25Q128JVSM).

The situation with RAM is more interesting. Officially, hAP ac2 claims 128 MB of RAM. At the same time, the first batches are equipped with 256 MB Nanya NT5CC128M16IP-DI chips.

233 MB is available to the end user. Mikrotik confirmed this fact, but they will not correct the description and characteristics for hAP ac^2, because There are batches with 128 MB. Someone from the logistics department screwed up big time.
So far, we have not come across a single device with 128 MB; all the copies we tested were equipped with 256 MB of RAM.
The hAP ac2 platform will be partially used in the RB450Gx4, although it is based on the IPQ-4019 with disabled wireless interfaces. The cost of the board will be almost twice that of the device under test. In return, Mikrotik offers 1 GB of RAM, 512 MB NAND Flash, Level 5 license and microSD support.
hAP ac 2 performance when working with L2TP/MPPE
Currently, there is a fairly wide range of possibilities for combining remote networks into a single computer network. The most popular tools are PPTP, L2TP, OpenVPN and IPsec.
The PPTP protocol is the oldest and most insecure, at the same time, oddly enough, the overwhelming number of Mikrotik users use the outdated pptp protocol for remote connections. Due to this protocol completely outdated and even in Apple devices Its support has been discontinued, we will not test this protocol.
The most optimal protocols are IPsec and OpenVPN.
IPsec is one of the most secure network interconnection methods that exists today. Featuring strong AES encryption with support for 128 and 256-bit keys, this protocol ensures the highest reliability and confidentiality of transmitted data that may be critical to business and government agencies. Today, even using the power of supercomputers, it would take billions of years to decrypt data encrypted using AES. Cons this method also available - the presence of external static IP at both ends of the connection and high requirements for the hardware platform. In principle, an IPsec connection is also possible between dynamic IPs, although in this case you will have to reconfigure the parameters every time one of the addresses changes. With the hardware platform, everything is also not so simple; entry-level budget RouterBOARDs can provide, at best, 10-20 Mbits with a full CPU load.
More advanced devices such as RB750Gr3, RB850Gx2 (discontinued), RB450Gx4, RB3011, RB1100AHx2, RB1100AHx4 and CCR1009 are capable of providing more high speed when working with IPsec. With the advent of hAP ac2, this list can be supplemented with one more model, but first things first.
There is also the possibility of using L2TP in conjunction with IPsec; the main advantage of this combination is high security, speed and ease of configuration, as well as greater loyalty to NAT on the end client side. Of the serious shortcomings this option It should be noted that there are very high requirements for the hardware platform; perhaps L2TP/IPsec is the most demanding protocol. This is due to double data encapsulation and the need for encryption.
The OpenVPN protocol, which is based on the OpenSSL library and the SSL/TLS protocols, does not have these shortcomings. OVPN itself is extremely flexible in configuration and even allows you to mask traffic as regular HTTPS, making it possible to bypass all kinds of restrictions on the part of the provider. Typically, OVPN is faster than IPsec and still supports a variety of encryption algorithms, including AES. This method still has disadvantages - more complex setup and high hardware requirements (as for IPsec).
For our part, to begin with, we will test L2TP with standard MPPE 128-bit encryption.
L2TP is more reliable and secure compared to the previous generation protocol - PPTP. We strongly recommend that you abandon the use of PPTP in favor of more modern protocols. If you do not have the ability and/or desire to use OVPN/IPsec/L2TP+IPsec, we recommend using L2TP/MPPE.
The main recommendation for increasing the security of L2TP/MPPE is to use very long passwords consisting of a set of random letters (with different layouts), numbers and special characters. The use of “dictionary” passwords is not recommended, since L2TP/MPPE has a number of shortcomings that allow the use of dictionary password guessing methods, which ultimately leads to a decrease in the security of a 128-bit key, making it equivalent to a 56-bit key (). In any case, it is much better than using PPTP.

As a pair for hAP ac2, we chose the proven CCR1009 platform, namely the .

It is the most affordable representative of the CCR line, which has a powerful 9-core Tile Gx processor and 1 GB of RAM. This combination provides high performance and the ability to process up to 2.5 Gbit of IPsec traffic.
During the testing process, stability and reliability under high loads were additionally checked; performance data is indicated for user traffic (useful traffic), an average sample was taken into account. Peak performance values are not taken into account in calculating the average if their duration is less than 30 seconds.

On both sides, PCs with iperf are used as traffic generators, which provides more reliable values and flexibility than the built-in BTest.
CCR1009 - WAN IP 192.168.106.20 / VPN 10.0.0.1 / LAN 192.168.1.0
hAP ac2 - WAN IP 192.168.106.30 / VPN 10.0.0.2 / LAN 192.168.2.0
For CCR1009, manual configuration was used, similar to defconf on low-level devices. ETH1 (not Combo) is used as WAN, standard Firewall rules are used, port 1701 is additionally open.

The L2TP Server configuration was based on a standard profile with encryption, the MTU was not changed, and the “Allow Fast Path” option was additionally activated.
All legacy authentication methods MSCHAP1, CHAP and PAP are disabled, only MSCHAP2 (MS-CHAPv2) is active.

In modern realities, it is better not to use compression to achieve maximum performance.
On the client side, the settings are similar, the default profile with encryption is used, as well as the “Allow Fast Path” option.

Routing to remote network provided by a static route in combination with NAT masquerade, default route is not used.
On both devices, the Firewall is configured with fasttrack connection for established and related connections.

The output is a classic combination of 2 networks based on L2TP/MPPE


Depending on the direction of traffic and configuration, CCR loads 1 core or distributes calculations among all 9 cores. For example, when sending data from CCR, 1 core is used, while when receiving data for decryption, all cores are loaded evenly.

Exchange of 1400 byte packets, TCP mode
The first throughput test is carried out for packets of 1400 bytes.
The average performance of a 1-stream test is 112 Mbit for receiving and 128 Mbit for sending.


When the number of sessions increases to 10, the speed changes to 111 and 170 Mbit, as we see, there is an increase in performance for sending with an increase in the number of sessions.

For Download (reception) there is no special increase, regardless of the size of the packages. Interestingly, in all of these cases, the IPQ-4018 load averaged up to 25%. Only 1 core is loaded, only occasionally the system unloads on the remaining cores - in multi-threaded modes.
We carry out a further test for Upload (sending) and increase the number of sessions to 20 and 100, as a result, the speed increases to 201 and 235 Mbit, respectively.


For additional monitoring during tests, the Tools - Profile tool was periodically used, with which we monitored the distribution of resources and their loading.
In fact, it clearly shows that as the number of simultaneous connections increases, RouterOS, albeit skewed, distributes part of the calculations to the remaining cores. Along with the increase in performance, the load on the CPU increases to 35-45%.
The last test in this block is for FDX (Full Duplex) with 10 counter connections in each direction, for a total of 10+10 sessions.

As a result, the total throughput amounted to 185 Mbit.
The final performance chart when working with 1400-byte packets looks like this:

Today I will introduce you short review to the router that I had been waiting for a long time (it was announced back in 2015) and finally got it. In short, I can say that for most users its rich capabilities will be unnecessary, but for those who want to get flexible settings home network There are practically no alternatives (for comparative money). If you are interested, welcome to cat.
To begin with, I will outline the background of the purchase, what prompted me to take Mikrotik
For a long time, my home router was the time-tested old Asus RT-16N. Overall very good router, which fully satisfied my needs for home internet, plus it provided fairly good Wi-Fi coverage. Firmware from Oleg was installed on it, and then from his followers, which significantly improved its performance and added a number of additional functions to the router. In general, for (approximately) 5 years, this long-liver provided my needs completely. However, relatively recently, due to work needs, I needed to raise the VLAN on the WAN port to provide access to the work network from home and to the home network from work. And here certain difficulties arose: Oleg’s firmware in the webmord does not provide such an opportunity, and after digging through ssh I was also unable to do this. After reading the forums and asking around, the great Google quickly came to the only solution for the RT-16N: install the OpenWRT firmware, which I successfully did. I managed to set up all the settings without any problems and everything worked, but two VERY unpleasant problems quickly emerged. The Asus company does not provide enthusiasts with access to control their hardware (which is understandable in principle) and therefore all alternative firmware uses either the basic system kernel from Asus with minor changes functionality (DD-WRT, firmware from Oleg, etc.), or they write something of their own (OpenWrt), but due to the lack of documentation and manufacturer support, they implement their commands in a non-optimal way. In my case this resulted in:
1. Big dances with a tambourine around WiFi since for a long time he agreed to rise only in the bg range at a speed of 54 M/bit and N did not start with any effort.
2. Much sadder: when the network load was high at a rate of 100 megabits, the router hit a maximum ceiling of 55-60 megabits with a processor load of 100%.
If you managed to more or less cope with the first problem by talking on the forums of VRT specialists and downloading third-party “drivers” for Wi-Fi and seemingly reviving the N band (although it works strangely: when you reboot the router, it drops the breeches and you have to raise Wi-Fi to manual mode+ the ability to create access lists by MAC addresses has disappeared). but in general, Wi-Fi is more or less moving.
There was no way to cope with the second problem, although multiple firewall rules were reduced to the required minimum, but it did not help: the download speed from the Internet did not rise above 60 (the speed inside the home network did not drop, but this is understandable - there is essentially no load there everything goes directly).
In general, taking into account all of the above, I gradually began to come to the conclusion that it was time to change the router, but after studying the market I realized that not everything is so simple. I wanted modern hardware that would be relevant for +N years and would provide good speed Internet in the future even more than 100 M/bit (such tariffs have already begun to appear, which means that in 2-3 years it will be commonplace with an affordable price), and of course I wanted a dual-band router with support for WiFi AC networks in the future.
It was useful to choose and realized that the choice with such requests is small. Stock firmware of common brands does not provide the flexible settings that I need (in most, even expensive routers, everything is limited to Vlan settings for IPTv multicast, which I don’t really need. This means I’ll have to sew again and again (possibly) have dances with a tambourine in the future. I wanted to take TpLink Archer 7, but I read in time that the AC mode is not yet available on OpenVrt, and whether it will be available in the future - I don’t know.
In general, I wanted something that would allow me to get everything I need using basic firmware and without hemorrhoids. And then I came across a mention on the Internet about the imminent (yup, imminent:) release of the subject. I got acquainted with the characteristics and realized - this is the router of my dreams. It can do everything you need from its RouterOS, in terms of settings it will satisfy any network management needs and in terms of hardware it is very promising (I hope its capabilities will be enough for me in the coming years).
Let's take a closer look at the capabilities of this miracle box:

As you can see, the hardware is very decent, and will cover all the requests of most users. You can take a look at the guts of the router (to be honest, I didn’t disassemble my router, photos were found on the Internet)

In the figure: numbers 1,2 indicate built-in 2.4 GHz antennas, numbers 3, 4 indicate 5 GHz antennas. Underneath the epoxy are the UFL connectors to which antennas 5 and 6 (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) are connected. 

Router block diagram: 
CAPsMAN - Another opportunity from Mikrotik for country houses/offices
Starting with version 6.11, RouterOS introduced the CAPsMAN functionality - the ability to centrally manage access nodes.
That is, instead of configuring each such node separately, it is enough to configure one controller and then connect managed nodes to it. It is in this way, and not using WiFi repeaters that only repeat a signal already received with errors and increased latency over a wider coverage area, that you can quickly and easily organize seamless single network, capable of covering almost any object in size.
It is clear that the quality of such coverage will directly depend on the hardware capabilities of the central controller. When using three or four MikroTik hAP ac, for example, it will not be difficult to create a network that does not require re-login throughout the entire volume of a three-story country house (with a basement, attic and outbuildings) or an entire vast floor of a business center.
At the same time, thanks to the ability to receive and distribute supply voltage further down the chain via the Ethernet line (Poe In/PoE Out), such devices will allow you to do without redundant wires and additional load on electrical outlets.
To reliably cover extended (one, two or three dimensions) objects with a WiFi network, two alternative methods are used:
1. You can install in the center of such an object a really powerful universal router with several external antennas, with the ability to simultaneously create two or more non-overlapping communication channels in the 5 GHz range - and hope that this monster will confidently “finish off” all the way to the border of the calculated area " And if not, then try to increase its power with additional antennas, but simply increasing the number of antennas will not lead to an increase in total power: the developer can either make individual antennas more powerful, or increase their number, but not both. Accordingly, you can install a WiFi repeater at a great distance, but such a solution is fraught with inevitable deterioration in the quality of communication.
2. Another approach, Mikrotik with RouterOS - CAPsMAN, is directly opposite to the first. It provides for the organization of a two-level network consisting of one control router and several managed access nodes. Each of these devices will be cheaper than a monstrous, super-powerful Internet center. Their combination of reasonably distributed efforts will lead to the fact that along the entire covered length, or over the entire area, or throughout the entire volume, the level WiFi signal will remain approximately the same, and switching between access nodes mobile devices will occur seamlessly and unnoticed by both the user and applications.
The range of applicability of hAP ac is further expanded by the presence of an SFP port for installing a fiber optic communication module. Using an optical data delivery line to each access node allows you to expand the area WiFi coverage a single network configuration almost indefinitely, as long as the central router has enough computing resources to process all requests in a timely manner.
Well, now briefly about my own impressions:
This little box fully met my expectations, the speed is strictly according to the tariff, nothing is cut or lost. When I tested the 5 GHz network, the Wi-Fi speed within the network exceeded 100 megabits (115-120). Unfortunately, I don’t have a single speaker device at hand, so I’ll have to wait for the future to look into my home :) However, there is no urgent need for speakers right now - anyway, (my) Internet tariffs will not support it, so this technology is for the future .
As for the settings, you can really break your head by studying the tabs :) The tool is really flexible and allows any network perversions.
For example, this is how you can configure a guest grid:
And this is how you can deploy HotSpot:
I decided not to drag it here as a spoiler, after all, it doesn’t make sense to drag half the Internet here, sometimes links are enough. I am sure that if someone is interested, they will find any additional information.
Mikrotik turned out to be very interesting home router. The company has made a worldwide name for itself in network solutions for corporate needs, and now, apparently, its time has come to develop the home segment of the market, I am sure that they have prospects in this direction. In general, I am personally absolutely satisfied, the new router has started working on my home network, I hope it will serve me no less than the Asus. I’ll take my leave for this, if you have any questions, write.
Down there in the comments they rightly pointed out to me about the lack of photos of the purchase and suspected me of being an advertising agent :) Fair point. I didn’t take any photos of the parcel or unpacking, but I didn’t want a working device, since I didn’t have time to lay out the wires nicely - they stick out in different directions. The router was received just yesterday.
However, I understand that it looks like an order, so here are the photos of the purchase, don’t look at the wires - I’ll think about how to carefully wire everything up.


Well, in a couple of days I cleaned up a little and combed the wires:


Every day I find something interesting and NEEDED in the router settings... In general, now I’m delving into the manuals - I really don’t regret the purchase for a second. Good luck friends!
I'm planning to buy +83 Add to favorites I liked the review +36 +87Mikrotik routers for a long time remained devices for professionals, but as the functionality of RouterOS grew, the web configurator also developed, becoming more user-friendly.
In Ukraine and Russia, among advanced users, Mikrotik became known thanks to its line of routers RB750 and RB951. Against the backdrop of foreign currency fluctuations (in Russia the rate increased by 2 times, in Ukraine by 3 times), Mikrotik routers have further strengthened their position in the market of inexpensive devices, both for home and small (medium) offices.
If you want to learn how to set up MikroTik, we suggest you go through. More detailed information can be found at the end of this publication.
For 700 UAH. in Ukraine you can now buy an entry-level router, the average router will cost 1200-1500 UAH, not to mention top-end solutions, the price of which exceeds several thousand hryvnia.
For 1500 UAH. Now you can buy the RB-951 Ui-2HnD (although before the crisis its price tag was 700 UAH), which can give odds to any Asus/D-Link/TP-Link/Linksys/Zyxel/Netgear/Tenda/Netis router, etc. .d. in this price range.
However, not every user can and is ready to pay that amount for a home SOHO router (Small Office, Home Office). And here Mikrotik has something to offer!
The new name is purely a marketing ploy to attract the average home user, because the purchase price for the new product starts at $21.95 (about 550 UAH at the current exchange rate). Of course, they won’t sell it to you for that price; at retail you should expect a new product from 700 UAH. and higher.
It would seem, what can you expect from a device for $22? After all, for that kind of money you can only buy... TL-WR741ND, Asus RT-N12, TL-WR841ND, Keenetic Start or TL-WR743 ND - and that’s all. You can't buy anything else for this money, from the popular products sold.
At the moment, pre-order is being carried out and it is very difficult to get hAP lite at retail for a reasonable price. We managed to receive one copy for review and testing, for which we express our deep gratitude to the VS KOM company.

Mikrotik hAP lite delivery kit
Delivery is carried out in standard Mikrotik packaging - a box made of thick brownish cardboard, without advertising, without color pictures. All that is on the box is the manufacturer’s logo and name, the name of the line, a sticker with the model name (MAC addresses, serial number).
Also printed on the back of the box is a short Quick Setup (Quick Guide) consisting of 4 steps:
- connect the Internet to port 1;
- connect the PC to port 2-5 (misspelled! we only have 4 ports);
- On your PC, set to receive settings automatically;
- enjoy using.
The box itself small sizes– 185 x 120 x 55 mm. For comparison, the box from RB951Ui-2 hnD has dimensions of 195 x 140 x 55 mm.
Inside the box is the router itself, the power supply and a leaflet with brief information about the device, its characteristics and how to access the web configurator.
There are no patch cords, bolts for fastening, advertising materials, software disks, manuals - there is none of this, as in other Mikrotik products. In principle, this is for the better; most users do not need this, with the possible exception of a patch cord. But the price tag on such packaging and configuration is significantly reduced.
In the end, you are buying a router, not waste paper for it. You can easily find everything you need on the Internet.
What can Mikrotik hAP lite offer us?
NOTE! We apologize in advance for the quality of the photos. Unfortunately, we did not have the opportunity to take photos in greenhouse studio conditions. If you have an “extra” Softbox (Lightbox) with the “correct” lighting, we will not refuse such a gift!


In short, at first glance the hAP lite is a simplified RB951-2n - and this is not entirely true.
The device body continues the traditions of the RB951 / RB750. If we compare the dimensions with the RB951 Ui-2HnD, the hAP lite is simply 5 cm shorter (9 cm versus 14 for the older model), otherwise the width and height are identical (115 x 30 mm).
The device is very compact, smaller in size than competing home routers.
The front panel contains all communication ports, indicators, power socket and reset button. There is nothing on the other panels of the device. With the exception of the right panel - it has a plug for USB, which is not here (but more on that later).


Regarding the RESET jumper, there are 4 possible use cases:
- press for up to 2 sec. activates WDS;
- press 5 sec. (before flickering starts) – reset to factory settings;
- press 10 sec. – transfer to CAPs;
- press 15 sec. (the indicators will go out) – installation of RouterOS via Netinstall. For example, in case incorrect installation, reinstallations, settings, or when the administrator password is lost.
The bottom panel contains a sticker with the model name, MAC addresses, and serial number. The legs are elastic and anti-slip.

In addition to the ventilation holes, back cover There are also 2 cross-shaped holes for wall mounting. This solution allows you to hang the device vertically in 4 variations, while most competitors, at best, provide L-shaped holes, which offer only 2 variations.
It's time to see the insides of hAP lite





The heart of the device is powerful processor QCA9531 (Small MIPS, made in Taiwan) with an operating frequency of 650 MHz. RAM capacity – 32 MB DDR400 (SAMSUNG K4H561638N-LCCC chip).

For storage software and settings, a Winbond 25Q128 FVSG chip (128 Mbit SPI FLASH, 8-SOIC, 104 MHz) with a capacity of 16 MB is used.
As can be seen from the photo, the board has miniature dimensions, electrolytic capacitors no, in principle (hello competitors!), and the processor itself, with a frequency of 650 MHz, does not even have a heatsink - it simply does not need one.

There is nothing on the back side of the board, although the remaining flux after soldering could be washed off. However, it’s not critical, Keenetic Lite the situation is similar. Fortunately, the flux is acid-free and non-conductive, so this is more of an aesthetic remark.
The device is equipped with only 4 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet Auto-MDI/X ports: one WAN port and 3 LAN ports. The ports are of high quality, with a metal shield, so it is possible to use shielded twisted pair (STP - Shielded twisted pair).
Power is connected via a microUSB socket from a 5V power supply. You can use the charger from any new mobile phone as a power source for this router if something happens to the original power supply.
The radio module is built into the QCA9531-BL3A and naturally does not support 5 GHz, it operates only at a frequency of 2.4 GHz according to the 802.11 b/g/n standard, the transmitter power is 158 mW (22 dBm). MIMO 2x2 is implemented, so the device uses 2 antennas, both internal PIF at 1.5 dBi. At the output of the radio module, for each channel, there is protection against static electricity (ESD) up to 10 kV.
Unfortunately, MMCX UFLs are not soldered on the board, so you can immediately forget about the RP-SMA pigtail and external antenna. The first versions had a service connector, presumably Hirose MS-156, for which there is an MS-156C-LP-068 pigtail (by the way, the latter has a mean time between failures of only 30 physical connections and disconnections). In retail deliveries, as in our copy, this connector is no longer soldered.
Soldering will also have to be abandoned due to the very small size of the tracks, except on soldering station under a magnifying glass, which of course will void the warranty.
Channel speed (theoretical physical limit) over Wi-Fi up to 300 Mbit/s – real speed will be about 110 Mbit/sec.

The power of the transmitter should not be intimidating, it is enough even for a 3-4 room apartment or a small office, the main thing is less concrete and load-bearing walls :)
The indicators are a standard set: one LED for each port, 1 LED displays power (PWR), 1 custom LED indicator (“ACT”) displays WiFi activity.
Overall, not bad. And what do you think controls this hardware? RouterOS with Level 4 license!
What does it mean? This means that inside we have a complete stuffing of VLAN, NAT, DNS, DHCP, Port Forwarding, PPP client/server, UPnP, WebProxy, SNMP, FTP, MESH, BGP, MPLS, intelligent shaper, traffic prioritization (advanced custom QoS) and much more! There is support for CAPsMAN.
However, Small MIPS imposes limitations. RouterOS for hAP lite is still a somewhat stripped-down version.
At the same time, as before, you can reassign any port - do you want 2 WAN? Or 3 at once? RouterOS will fulfill your every whim!
How else does hAP lite differ from its older brothers?
Have you noticed how the power is supplied? A powerful power supply cannot be connected to such a connector. But he doesn’t need it, because the router does not have a PoE function - our baby’s power consumption is only 3 W. For example, the older brother RB951Ui-2HnD can not only receive power via PoE, but also supply it to another device via the 5th port.
There are significantly fewer ports, and without gigabit support.
Unfortunately, the router does not support USB. On the case itself, of course, there is a plug for USB, but it is only for those cases if in the future you buy another RouterBOARD board and insert it into the case from hAP lite. Based on the name “hAP lite”, it is possible that more advanced versions “hAP Pro”, “hAP Plus” or “hAP Turbo” with USB, Gigabit, PoE, 5 GHz, etc. will appear.
Mikrotik has always been distinguished by its universal cases. Even the RB951 Ui-2hnD has plugs for RP SMA, but without “surgical” intervention external antennas don't screw it in there.
So...what am I talking about? For 22 USD you get many times more than any other router of this type will give you price category- nothing else matters. If you are looking for shortcomings, there are none, and if you find them, there is always a more advanced one for you. the lineup for a higher price.
Before you start testing

By default, the device address is 192.168.88.1, login is admin, password is empty. Nothing new for those who have dealt with Mikrotik before.
On the box itself the manufacturer warns us about this. That before using the device, you should update its RouterOS to latest version. Let's do so!
Since our copy came with RouterOS 6.25 out of the box, we will update it to 6.27 (the latest at the time of publication of the review).


In connection with all of the above, I still recommend choosing the “WISP AP” mode. However, in this case, the UPnP option, which is responsible for automatically configuring ports (for example, for a torrent client), will disappear from the QuickSet settings. To activate it, go to “IP – UPnP” and activate the “Enabled” option. In the “Interfaces” submenu, set “bridge-local” as “internal”, and “ether1-gateway” (or pope/pptp-out1, if you have Internet via VPN) as “external”.



What is in RouterOS on Mikrotik hAP lite?

This question interests many. In this regard, below is a list of sections and subsections of the WebFig v6.27 menu.
- Quick Set
- CAPsMAN
- Wireless
- Interfaces (support for VRRP, Bridge, EoIP, IP Tunnel, VLAN, Bonding, Mesh, VPLS, Traffic Eng Interface, Virtual Ethernet, GRE Tunnel, PPTP Server/Client, PPPoE Server/Client, L2TP Server/Client, OVPN Server/Client, SSPT Server/Client, VirtualAP, WDS, Nstreme Dual)
- Bridge
- Switch
- IP (ARP, Accounting, Addresses, Cloud, DHCP Client, DHCP Relay, DHCP Server, DNS, Firewall, Hotspot, IPsec, Neighbors, Packing, Pool, Routes, SNMP, Services, Settings, Socks, TFTP, Traffic Flow, UPnP, Web Proxy)
- Routing (BFD, BGP, Filters, MME, OSPF, Prefix Lists, RIP)
- System (Auto Upgrade, Certificates, Clock, Console, Drivers, Health, History, Identity, LEDs, License, Logging, Packages, Password, Ports, Reboot, Reset Configuration, Resources, Routerboard, SNTP Client, Scheduler, Scripts, Shutdown, Special Login, Users, Watchdog)
- Queues
- Files
- Radius
- Tools (BTest Server, Bandwidth Test, Email, Flood Ping, Graphing, IP Scan, MAC Server, Netwatch, Packet Sniffer, Ping, Ping Speed, Profile, SMS, Telnet, Torch, Traceroute, Traffic Generator, Traffic Monitor)
- New Terminal
Testing hAP lite

Since the router is positioned as a home router, we will test it “at home”.
The first WAN port is connected to one of the RB951Ui-2 HnD ports, which distributes the Internet. The devices have been configured to avoid IP conflicts. A PC and 2 more clients with low load were connected to the remaining free ports of hAP lite, including the RIPE Atlas v3 probe (/167-zond-ripe-atlas-v3.html).
The provider's tariff plan is 80 Mbit/sec, direct connection.
What should I load the router with? Of course, simultaneously torrents + online video + online music. More details about everything. The YouTube client is running on the smartphone, and a FullHD video is open. There are 4 downloads running on the PC, and there are additionally 2 active tabs in the browser - the first with online music, the second with YouTube videos in 4K format.

Why is this necessary? For many home routers, with such a load, online video and audio will slow down due to the torrent client. A typical situation: you download a torrent, and your brother or sister’s online video starts to slow down.
Mikrotik hAP lite coped with this test perfectly: on a PC, video and audio from VK worked without any problems, while video was played on the smartphone via Wi-Fi (up to 5 Mbit/sec). All remaining available speed was given to the torrent client. The total speed reached tariff plan Internet provider – 80 Mbit/sec. At the same time, the router processed an average of 12,500 packets per second.

A little later, we closed the video on the smartphone, and the video on the PC continued to play. The speed in the torrent client reached 9.5 MB/sec and... hit the disk subsystem (disk cache overload).
At this moment, on the WAN port, Mikrotik showed a speed of 91.2 Mbit/s for receiving and 3.9 Mbit/s for sending, for a total of over 13,800 packets/sec. Of course, it was possible to disable online video on a PC, then the number of packets would exceed 15 thousand/sec., however, even without this it is clear that hAP lite will cope with such a flow.

In general, I would like to note Good work QoS out of the box, for home use multiple devices, traffic prioritization is very important. And not every “home” router will cope with this task well. If you want to customize prioritization for yourself, the manuals will help you, hAP lite can do it!
Alternatively, check out the shaper testing from
MikroTik hAP Lite – one of the affordable and renowned routers on the market for similar equipment. Since 2016, the router has been extremely popular and is not inferior to more expensive and proven models.
What is the advantage of MikroTik hAP Lite compared to other routers, and why the model occupies a leading position, we will determine based on technical characteristics router and user reviews.
Set
For a review of the Mikrotik Hap Light router, watch the following video:
The product is supplied in a cardboard box, which contains:
- instructions;
- power supply 5V and 0.7A;
- Router BOARD hAP Lite (RB 941 2nD TC) is the official name of the model.
Design
The appearance of the router is shown in the picture:
Mikrotik hAP Lite has plastic case, consisting of white and blue parts. The front side of the case is equipped with ventilation holes. On the back side there are activity lights for the interface of four network ports, two diodes, a multifunction key and a Micro USB port (for power). To remove heat from the central chip area, the bottom of the router is equipped with ventilation holes.
The housing with connectors is shown in the picture:

The shape of the model's body allows the product to be used only in a vertical position.
Software and functionality
The functionality of MikroTik hAP Lite RB941 2nD corresponds to the high characteristics of the Qualcomm Atheros QCA9533 processor. The processor frequency is 650 MHz. Port transfer speed is 100 Megabytes. RAM– 32 MB (16 MB permanent).
The gain of the router's two antennas is 1.5 dB, which allows it to support speeds of up to 300 Mbps. The Wi-Fi power of the hAP Lite router is up to 158 mW (22 dB).
WiFi-router MikroTik hAP Liteoperates under the control of a specialized operating system– Router OS.
| Characteristics of MikroTik hAP Lite (RB 941 2nD TC) | |
|---|---|
| Type | Wireless router |
| Standard | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n |
| Limit connection speed, Mbit/s | 150 |
| Multiple SSID support | + |
| Connection interface (LAN port) | 3x10/100 Ethernet |
| Login (WAN port) | 1x10/100 Ethernet |
| Firewall | + |
| NAT | + |
| VPN (virtual network) support | + |
| DHCP server | + |
| Antenna type (internal/external) | internal |
| Number of antennas | 2 |
| MU-MIMO/MIMO support | -/+ |
| Web interface | + |
| Telnet | + |
| SNMP support | + |
| Dimensions, mm | 124x100x54 |
| Power (PoE/adapter) | -/+ |
| Bridge Mode | + |
| processor Qualcomm Atheros QCA9531 (650MHz), 32MB DDR RAM, RouterOS Level4 License | |
Settings
For video instructions on setting up the router, see the following video:
The Router OS system is presented at English language, and therefore, many users experience certain difficulties when setting up the Mikrotik hAP Lite router . We'll look at how to configure the router and set the required parameters below.
At the first stage, you need to do the following:
- Connect a router to your PC (tablet, laptop, smartphone). Activate power.
- Connect the Internet to the router. You can activate the connection by Wi-Fi networks. If this is not possible, connect the LAN port of the router and the network card PC.
- Connect to the Wi-Fi network “MikroTik”.
If the network password is valid, reset the settings.
Regardless of presence/absence network connection, you can move on to the next step. To go to the router settings, you should go to the page at 192.168.88.1. We will have access to the RouterOS control panel. On at this stage You need to make sure that the device is in “Home AP” mode.
How to find out what mode the router is operating in, look at the picture:

The list of parameters is divided into three blocks and looks like this:
- connection to the network (Internet);
- Wi-Fi network (Wireless);
- password to protect the system interface (System).
Settings for dynamic IP
Provided the Internet is already working via MikroTik hAP Lite in additional settings not necessary. Thanks to automatic connection, you can immediately set the Wi-Fi network parameters.
Contact your Internet service provider for information about your connection type (if you don't have a dynamic IP). You should also clarify whether your Internet provider allows you to bind by MAC address.
Provided there is a dynamic IP and no binding by MAC address, the router is fully operational at this stage.
If you need to bind by MAC address, you should specify the MAC address of the network equipment (either from your Internet service provider or in the “MAC address” field in the router settings). The equipment address is reflected in the MAC Address field.
Entering parameters when connecting PPPoE
How to connect can be seen in the picture:

This type of connection is not particularly popular. Here you should highlight the connection type “PPPoE” and indicate the username and password. Next, activate the “Reconnect” button and go to Wi-Fi settings networks. The data containing the username and password is provided by the Internet service provider.
Setting up a password and Wi-Fi network
Let's turn to the “Wireless” section (located on the left side of the page). You can change the Wi-Fi network name in the “Network Name” field. Next, in the “Country” menu that opens, indicate the password (“WiFi Password”).
This is what the window looks like where you can change the network name and update the password:

The password for accessing the Internet must contain at least eight characters. It is also recommended to indicate the user's region of residence.
Here you can also clarify the list of clients connected to the router and set the parameters of the guest Wi-Fi network. Before leaving the section, you should save the settings using the “Apply Configuration” button.
Password for the web interface
In order to protect the RouterOS interface from unauthorized persons, it is recommended to set a password. To do this, it is suggested to go to the “System” section (in the lower sector on the right). Next, enter the password in the “Password” and “Confirm Password” fields. To save the settings, use the “Apply Configuration” button.
The page for entering a new password looks like this:

At this stage, the user will be “kicked out” of the system. To log in again and gain access to the interface, you will need to enter again. given password. In addition to the password, you must enter the username (admin).
The login page looks like this:

Router in operation
Numerous positive reviews Owners of Mikrotik hAP Lite routers testify to the simplicity, but at the same time reliability of this router model. The undeniable advantages of the RB941 2nD TC router are:
- the ability to simultaneously connect an unlimited number of gadgets (the scale of connected devices does not have a negative impact on the operation of the router);
- price – the cost of the device does not exceed 1,500 rubles;
- compactness;
- functional operating system;
- support – regular updates;
- quality of execution;
- wireless signal strength;
- convenience and simplicity of the interface;
- Micro USB power;
- design.
Pay attention to functionality Mikrotik hAP Lite router and reviews of its work , we can confidently conclude that this model is still the best in its price segment.
So on this moment we have a standard configuration without network separation. In order to differentiate our local network, let's create a segment (part) of the network for children. To do this, select winbox→ Bridge(1)→Bridge(2)→plus(3)→General(4)→ from the menu and add the name bridge-child in the name(5) field. Let's save the changes - OK.
Let's prepare interfaces (ports) for inclusion in bridge-child. In our configuration, a fourth ether4 port and an additional children's wifi network will be configured for the child. This means that by connecting to the fourth port with a cable and/or to a children's network via WiFi, you will have children's access to the Internet through these interfaces.
Setting up a security profile for children WiFi networks. WinBox→Wireless(1)→Security Profiles(2)→plus(3)→General(4)→in the Name(5) field enter child→in the WPA(6) and WPA2(6) fields enter the future password for the Wifi children's network . Save the settings - OK.

Let's add new network wifi WinBox→Wireless(1)→Interfaces(2)→plus(3)→Virtual AP(4)→Wireless(5)→enter the name of the children's WiFi network in the SSID(6)→select security profile(7) for our network. Save the settings - OK.

Let's configure the ether4 interface. Winbox→Interfaces(1)→Interface(2)→double-click with the left button on ehter4(3) and enter the interface settings→select none in the Master Port(4) field. Apply the settings - OK.

Next, we will include our interfaces in the prepared bridge-child. Winbox→Bridge(1)→Ports(2)→plus(3)→add the ether4 (4) interface→to Bridge(5) bridge-child. We will do the same for the wlan2(6)(7) interface. Let's save all changes - OK.
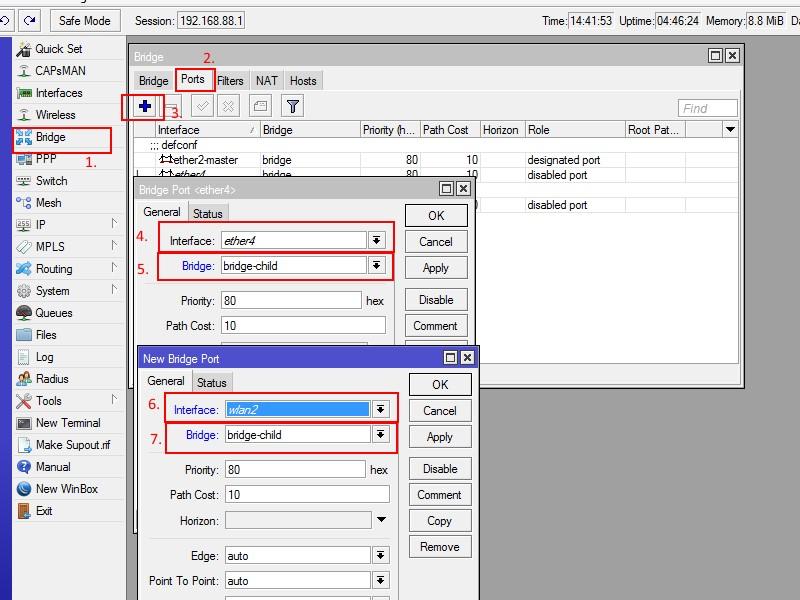
Let's assign an internal address to the bridge-child interface. WinBox→IP(1)→address(2)→plus(3)→fill in fields (4), (5), (6) according to the screenshot.

Now you need to assign a DHCP server to the children's network segment to automatic settings IP parameters of network clients. To do this, you need to Winbox→IP(1)→DHCP server(2)→DHCP(3)→DHCP Setup(4)→ select the bridge-child interface in the dhcp Server Interface(5) field.

After this, you need to click the Next button and follow the DHCP server setup wizard without changing anything. Once you reach the Select lease time window:

Here you need to change the standard lease time to 3d 00:10:00 and finish setting up the DHCP server.
If you did everything correctly, by this point you should have two network segments:
Children's network LAN-4; wifi Addressing - 192.168.99.0/24 Adult network LAN-2, LAN-3; wifi Addressing - 192.168.88.0/24
Now these two networks have no restrictions and are completely equal. To begin setting up restrictive functions for the children's network, you need to complete the preliminary settings of the router, namely:
- Set password and SSID (network name) for adult wifi network
- Set a password for the Admin user
- Update your router to the latest version.
If you find it difficult to do this yourself, you can find step-by-step instructions for setting these parameters in





